Juniper Apstra Terraform Provider- Store Remote State
Juniper Apstra Terraform Provider- Store Remote State
Now you have built, changed, and destroyed infrastructure from your local machine. This is great for testing and development, but in production environments you should keep your state secure and encrypted, where your teammates can access it to collaborate on infrastructure. The best way to do this is by running Terraform in a remote environment with shared access to state.
Terraform Cloud allows teams to easily version, audit, and collaborate on infrastructure changes. It also securely stores variables, including API tokens and access keys, and provides a safe, stable environment for long-running Terraform processes.
In this tutorial, you will migrate your state to Terraform Cloud.
Run terraform init to initialize your configuration directory and download the required providers. It is safe to re-run this command even if you have already done so in this directory.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % cat main.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
apstra = {
source = "Juniper/apstra"
version = ">= 0.28.0"
}
}
required_version = ">= 1.1"
}
provider "apstra" {
url = "https://admin:password@10.210.40.194:443"
tls_validation_disabled = true
blueprint_mutex_enabled = true
}
# This example creates an IPv4 Resource Pool with three allocations inside:
# - 3 blocks from RFC5737
#
# After creating the pool, it outputs the total number of
# IP addresses in the pool.
resource "apstra_ipv4_pool" "example" {
name = "RFC 5737 ranges"
subnets = [
{ network = "192.0.2.0/24"},
{ network = "198.51.100.0/24"},
{ network = "203.0.113.0/24"},
]
}
output "example_pool_size" {
value = format("pool '%s' is sized for %d addresses", apstra_ipv4_pool.example.name, apstra_ipv4_pool.example.total)
}
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
Init
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % terraform init
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Finding juniper/apstra versions matching ">= 0.28.0"...
- Installing juniper/apstra v0.42.0...
- Installed juniper/apstra v0.42.0 (signed by a HashiCorp partner, key ID CB9C922903A66F3F)
Partner and community providers are signed by their developers.
If you'd like to know more about provider signing, you can read about it here:
https://www.terraform.io/docs/cli/plugins/signing.html
Terraform has created a lock file .terraform.lock.hcl to record the provider
selections it made above. Include this file in your version control repository
so that Terraform can guarantee to make the same selections by default when
you run "terraform init" in the future.
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
Apply
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % terraform apply
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# apstra_ipv4_pool.example will be created
+ resource "apstra_ipv4_pool" "example" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = "RFC 5737 ranges"
+ status = (known after apply)
+ subnets = [
+ {
+ network = "192.0.2.0/24"
+ status = (known after apply)
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
},
+ {
+ network = "198.51.100.0/24"
+ status = (known after apply)
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
},
+ {
+ network = "203.0.113.0/24"
+ status = (known after apply)
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
},
]
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Changes to Outputs:
+ example_pool_size = (known after apply)
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
apstra_ipv4_pool.example: Creating...
apstra_ipv4_pool.example: Creation complete after 1s [id=aaf76153-da61-4118-83b8-20d219130076]
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
example_pool_size = "pool 'RFC 5737 ranges' is sized for 768 addresses"
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
With this, Terraform provisioned an IPv4 pool in Juniper Apstra and stored data about the resource in a local state file.
Set up Terraform Cloud
If you have a HashiCorp Cloud Platform or Terraform Cloud account, log in using your existing credentials.
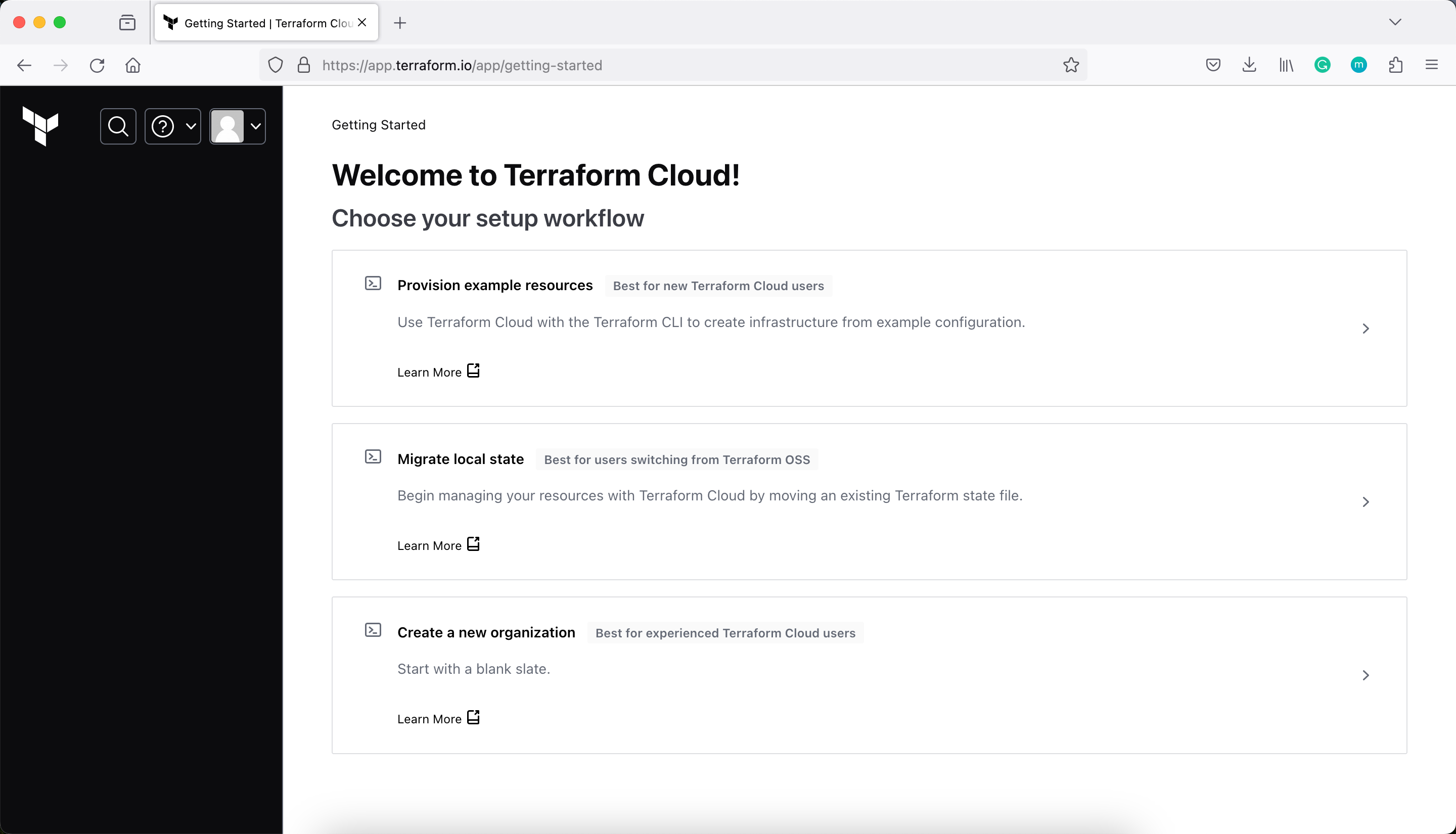
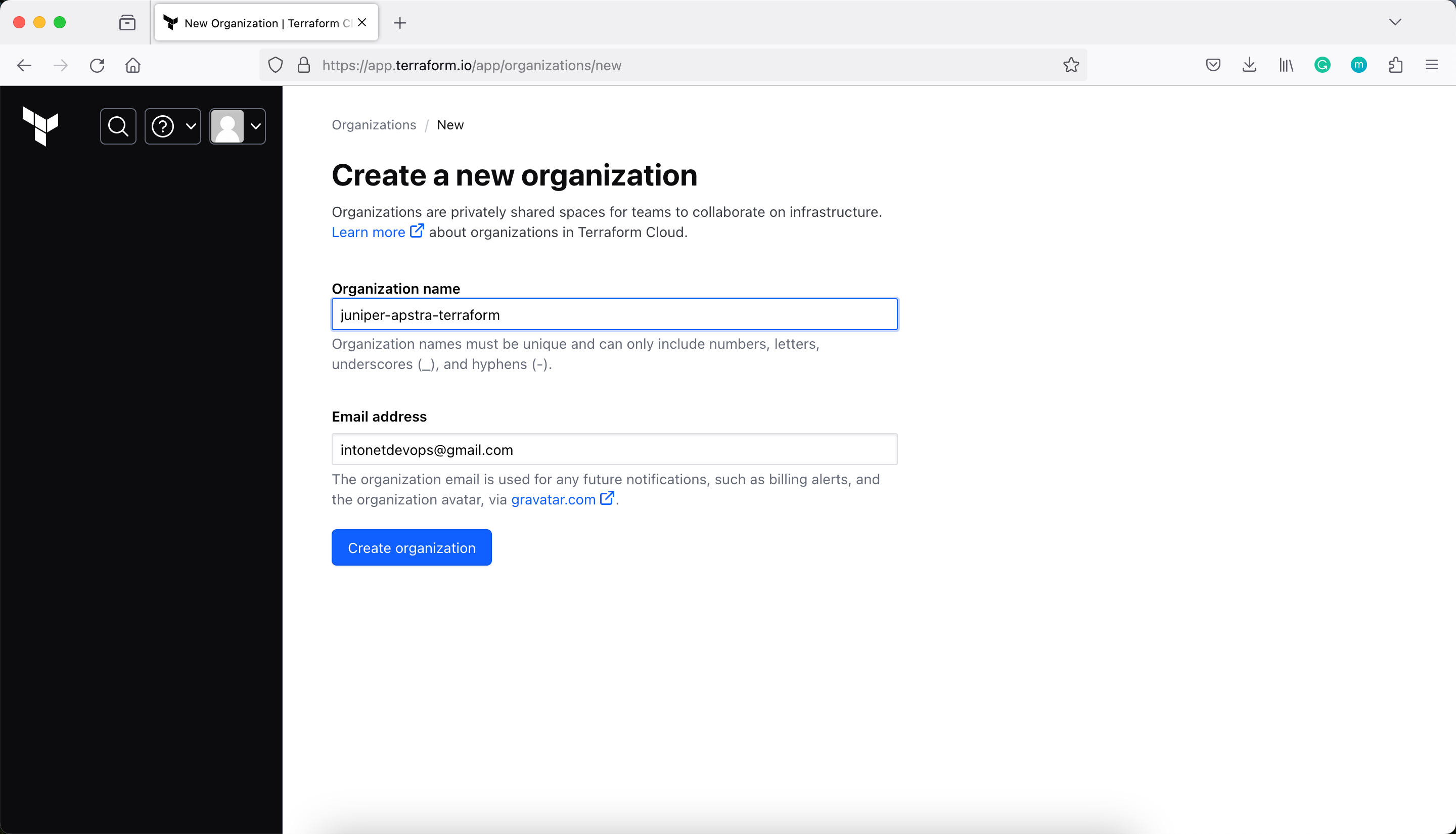
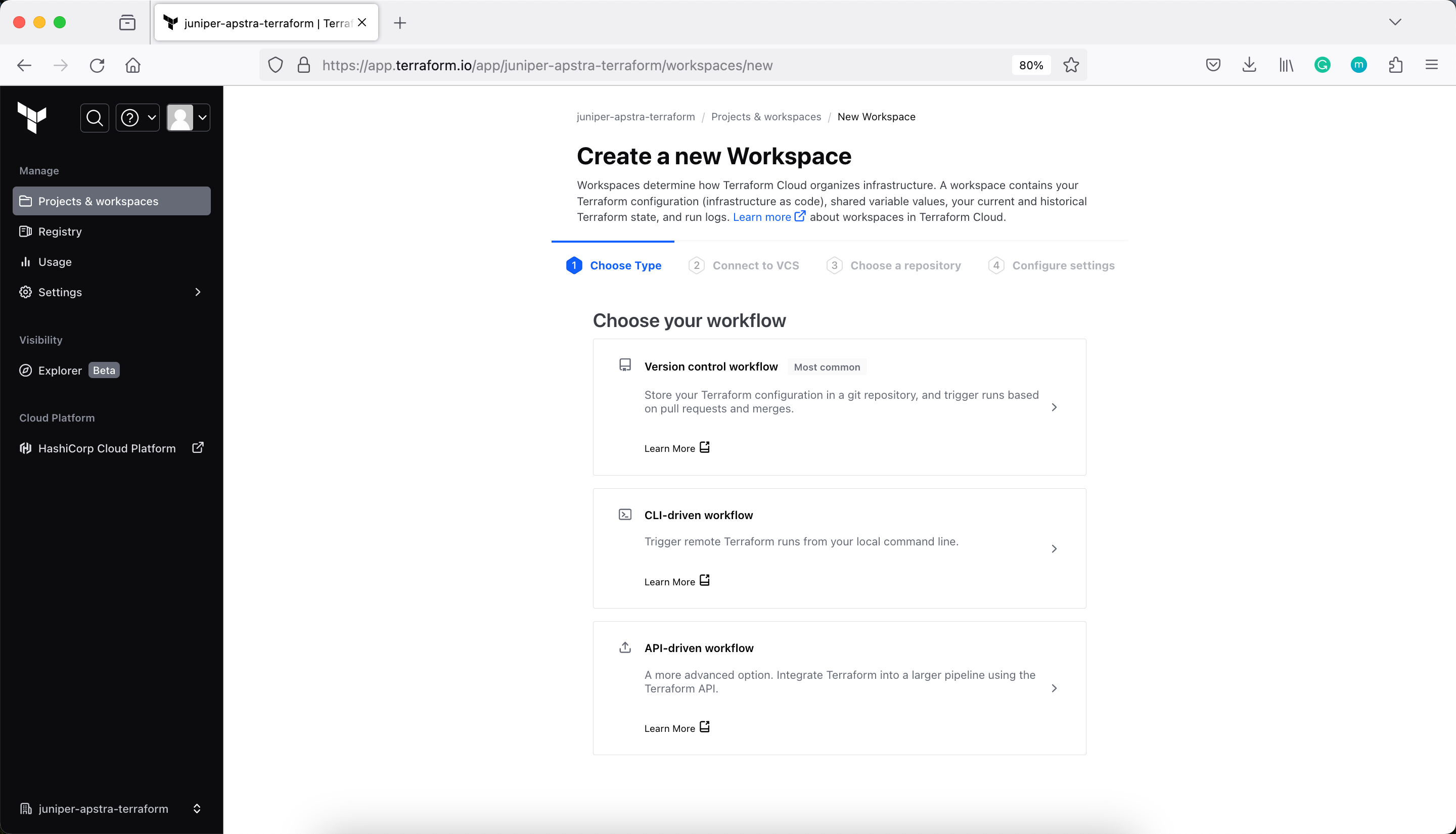
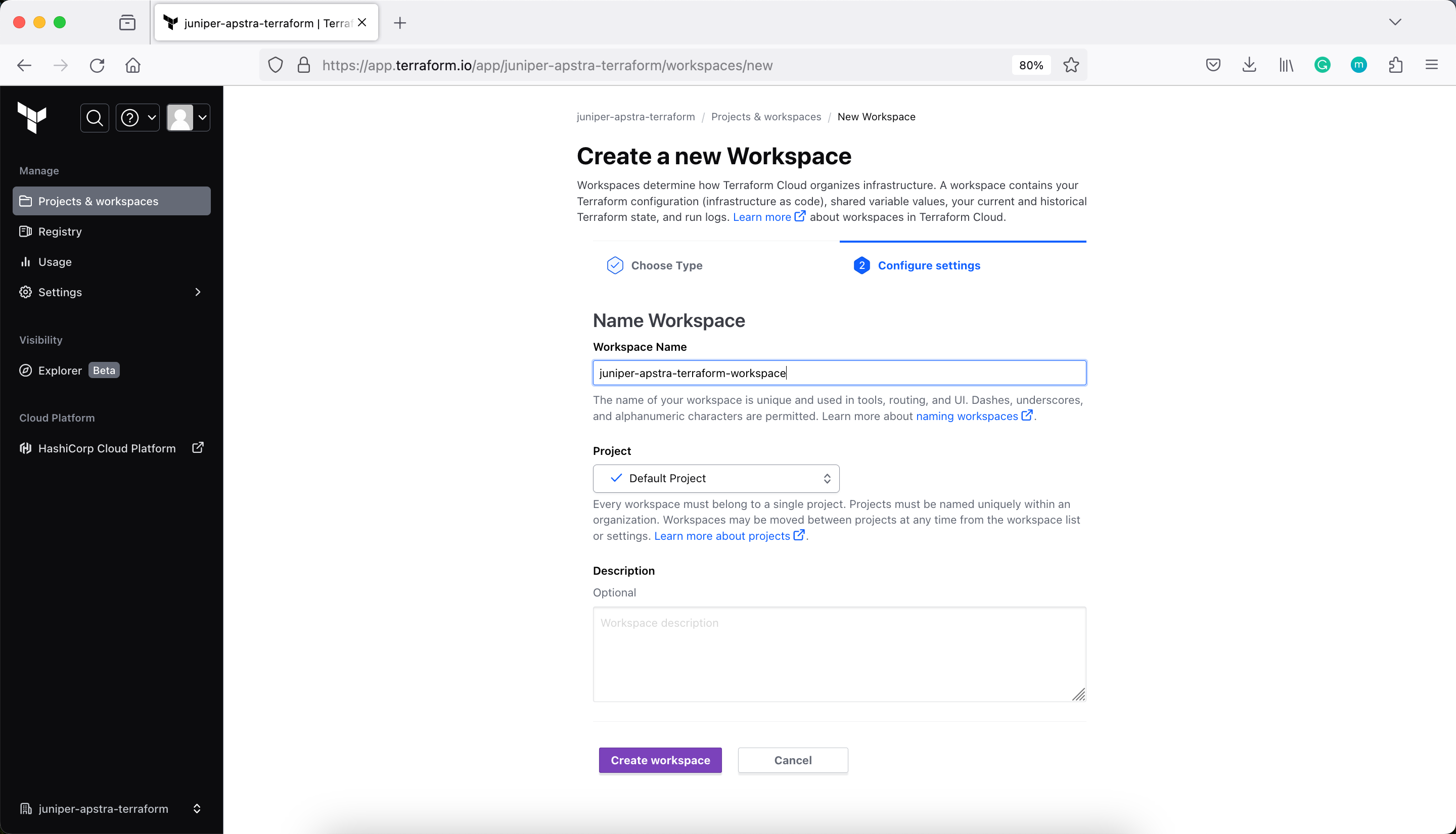
Next, modify main.tf to add a cloud block to your Terraform configuration, and replace organization-name with your organization name.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % cat main.tf
terraform {
cloud {
organization = "juniper-apstra-terraform"
workspaces {
name = "juniper-apstra-terraform-workspace"
}
}
required_providers {
apstra = {
source = "Juniper/apstra"
version = ">= 0.28.0"
}
}
required_version = ">= 1.1"
}
provider "apstra" {
url = "https://admin:ApstraT3rraf0rm!@10.210.40.194:443"
tls_validation_disabled = true
blueprint_mutex_enabled = true
}
# This example creates an IPv4 Resource Pool with three allocations inside:
# - 3 blocks from RFC5737
#
# After creating the pool, it outputs the total number of
# IP addresses in the pool.
resource "apstra_ipv4_pool" "example" {
name = "RFC 5737 ranges"
subnets = [
{ network = "192.0.2.0/24"},
{ network = "198.51.100.0/24"},
{ network = "203.0.113.0/24"},
]
}
output "example_pool_size" {
value = format("pool '%s' is sized for %d addresses", apstra_ipv4_pool.example.name, apstra_ipv4_pool.example.total)
}
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
Login to Terraform Cloud
Next, log into your Terraform Cloud account with the Terraform CLI in your terminal. Confirm with a yes and follow the workflow in the browser window that will automatically open. You will need to paste the generated API key into your Terminal when prompted.
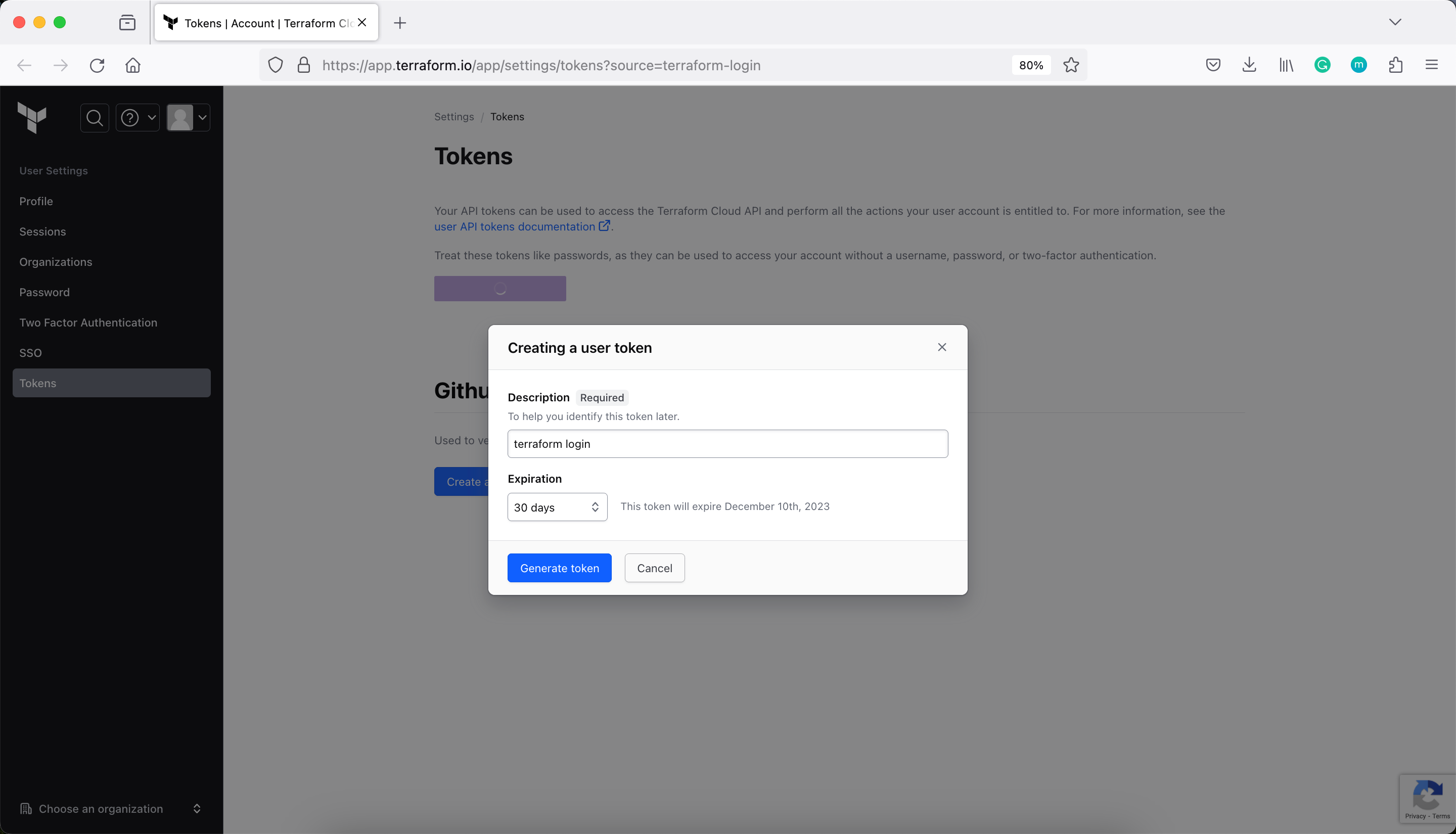
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % terraform login
Terraform will request an API token for app.terraform.io using your browser.
If login is successful, Terraform will store the token in plain text in
the following file for use by subsequent commands:
/Users/pradga/.terraform.d/credentials.tfrc.json
Do you want to proceed?
Only 'yes' will be accepted to confirm.
Enter a value: yes
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Terraform must now open a web browser to the tokens page for app.terraform.io.
If a browser does not open this automatically, open the following URL to proceed:
https://app.terraform.io/app/settings/tokens?source=terraform-login
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Generate a token using your browser, and copy-paste it into this prompt.
Terraform will store the token in plain text in the following file
for use by subsequent commands:
/Users/pradga/.terraform.d/credentials.tfrc.json
Token for app.terraform.io:
Enter a value:
Retrieved token for user intonetdevops
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
----- -
--------- --
--------- - -----
--------- ------ -------
------- --------- ----------
---- ---------- ----------
-- ---------- ----------
Welcome to Terraform Cloud! - ---------- -------
--- ----- ---
Documentation: terraform.io/docs/cloud -------- -
----------
----------
---------
-----
-
New to TFC? Follow these steps to instantly apply an example configuration:
$ git clone https://github.com/hashicorp/tfc-getting-started.git
$ cd tfc-getting-started
$ scripts/setup.sh
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
Initialize Terraform
Now that you have configured your Terraform Cloud integration, run terraform init to re-initialize your configuration and migrate your state file to Terraform Cloud. Enter “yes” when prompted to confirm the migration.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % terraform init
Initializing Terraform Cloud...
Do you wish to proceed?
As part of migrating to Terraform Cloud, Terraform can optionally copy your
current workspace state to the configured Terraform Cloud workspace.
Answer "yes" to copy the latest state snapshot to the configured
Terraform Cloud workspace.
Answer "no" to ignore the existing state and just activate the configured
Terraform Cloud workspace with its existing state, if any.
Should Terraform migrate your existing state?
Enter a value: yes
Acquiring state lock. This may take a few moments...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Reusing previous version of juniper/apstra from the dependency lock file
- Using previously-installed juniper/apstra v0.42.0
Terraform Cloud has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform Cloud. Try running "terraform plan" to
see any changes that are required for your infrastructure.
If you ever set or change modules or Terraform Settings, run "terraform init"
again to reinitialize your working directory.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
Verify the Workspace for Resources and Outputs
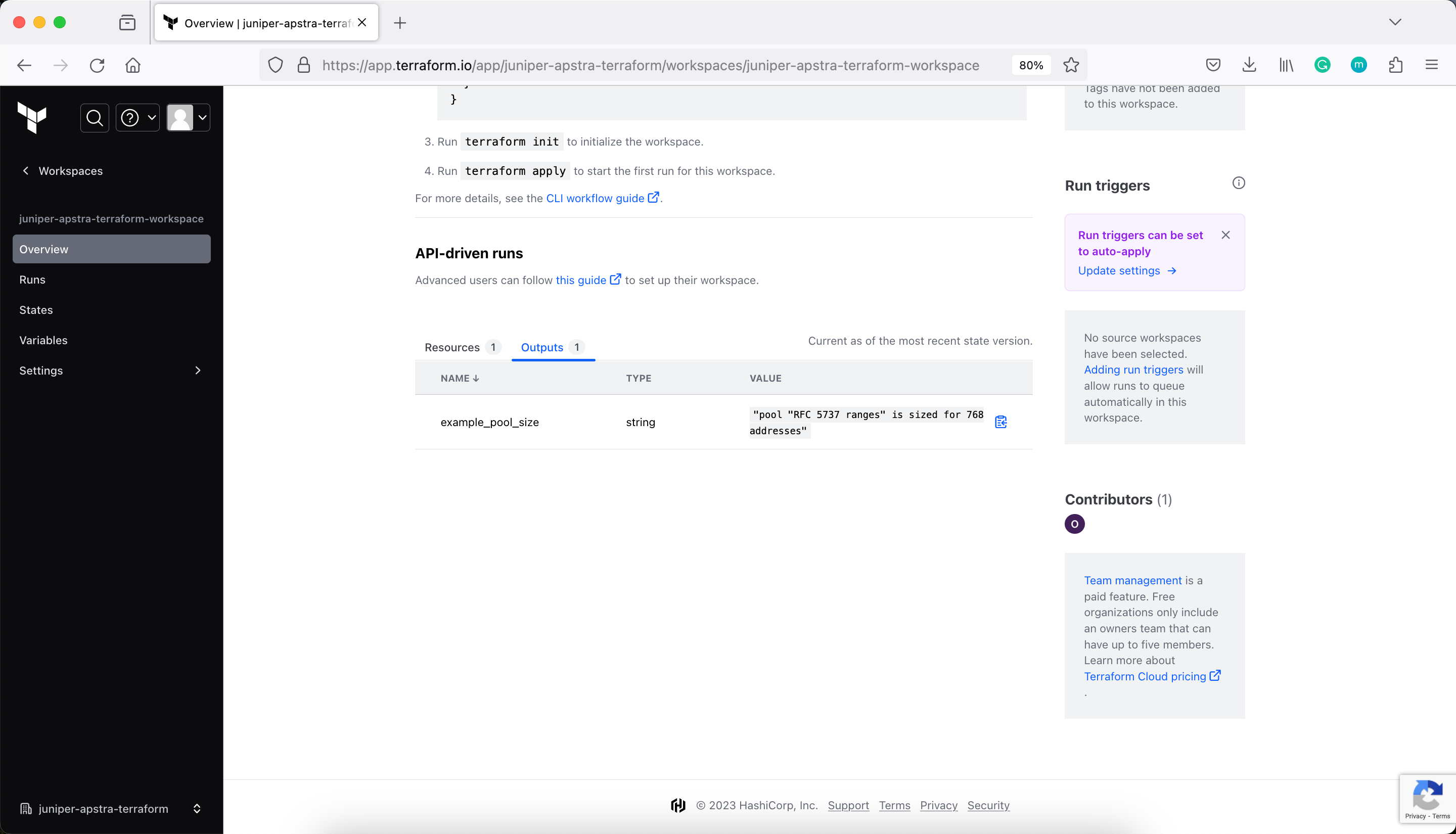
Apply the configuration
Now, run terraform apply to trigger a run in Terraform Cloud.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % terraform apply
Running apply in Terraform Cloud. Output will stream here. Pressing Ctrl-C
will cancel the remote apply if it's still pending. If the apply started it
will stop streaming the logs, but will not stop the apply running remotely.
Preparing the remote apply...
To view this run in a browser, visit:
https://app.terraform.io/app/juniper-apstra-terraform/juniper-apstra-terraform-workspace/runs/run-GNBn9uDUKNAgiuLi
Waiting for the plan to start...
Terraform v1.6.3
on linux_amd64
Initializing plugins and modules...
╷
│ Error: unable to create client
│
│ with provider["registry.terraform.io/juniper/apstra"],
│ on main.tf line 17, in provider "apstra":
│ 17: provider "apstra" {
│
│ error creating apstra client - error calling http.client.Do for url
│ 'https://10.210.40.194:443/api/versions/api?async=full' - Get
│ "https://10.210.40.194:443/api/versions/api?async=full": context deadline
│ exceeded
╵
Operation failed: failed running terraform plan (exit 1)
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
Since my Juniper Apstra does not have external connectivity, Terraform Cloud could not connect and hence the Operation failed running running terraform plan. But, from the first line, you can tell that the apply in coming from the Terraform Cloud (remote), the output is streamed locally.
Terraform is now storing your state remotely in Terraform Cloud. Remote state storage makes collaboration easier and keeps state and secret information off your local disk. Remote state is loaded only in memory when it is used.
Destroy your infrastructure
Make sure to run terraform destroy to clean up the resources you created in these tutorials. Terraform will execute this run in Terraform Cloud and stream the output to your terminal window.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % terraform destroy
Running apply in Terraform Cloud. Output will stream here. Pressing Ctrl-C
will cancel the remote apply if it's still pending. If the apply started it
will stop streaming the logs, but will not stop the apply running remotely.
Preparing the remote apply...
To view this run in a browser, visit:
https://app.terraform.io/app/juniper-apstra-terraform/juniper-apstra-terraform-workspace/runs/run-wWZq2agLTeM8g5id
Waiting for the plan to start...
Terraform v1.6.3
on linux_amd64
Initializing plugins and modules...
╷
│ Error: unable to create client
│
│ with provider["registry.terraform.io/juniper/apstra"],
│ on main.tf line 17, in provider "apstra":
│ 17: provider "apstra" {
│
│ error creating apstra client - error calling http.client.Do for url
│ 'https://10.210.40.194:443/api/versions/api?async=full' - Get
│ "https://10.210.40.194:443/api/versions/api?async=full": context deadline
│ exceeded
╵
Operation failed: failed running terraform plan (exit 1)
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
This also failed for the same reason of no external connectivity from Juniper Apstra.
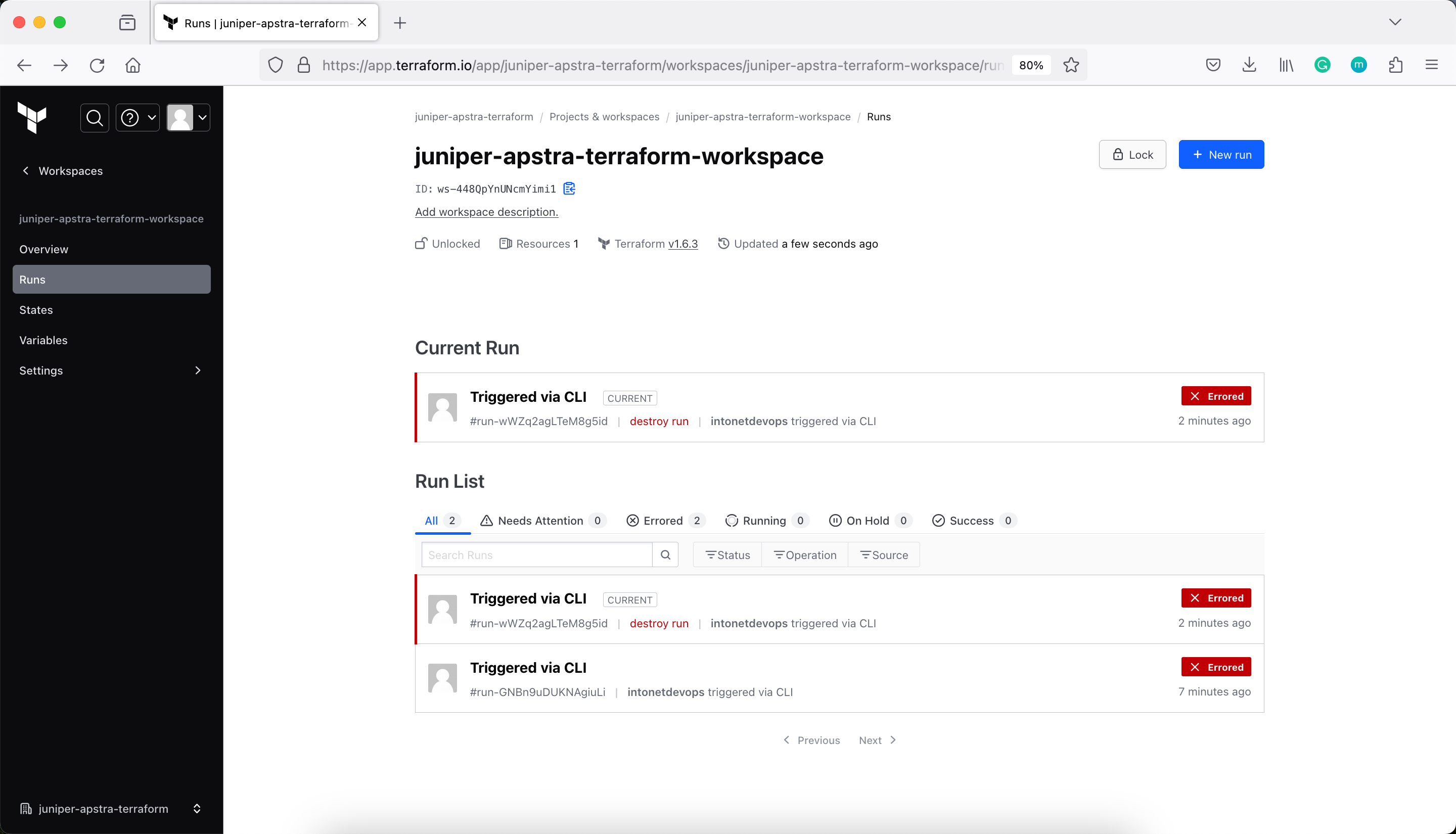
Modify the Backend from Cloud to Local (remove the cloud block from Terraform)
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % cat main.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
apstra = {
source = "Juniper/apstra"
version = ">= 0.28.0"
}
}
required_version = ">= 1.1"
}
provider "apstra" {
url = "https://admin:ApstraT3rraf0rm!@10.210.40.194:443"
tls_validation_disabled = true
blueprint_mutex_enabled = true
}
# This example creates an IPv4 Resource Pool with three allocations inside:
# - 3 blocks from RFC5737
#
# After creating the pool, it outputs the total number of
# IP addresses in the pool.
resource "apstra_ipv4_pool" "example" {
name = "RFC 5737 ranges"
subnets = [
{ network = "192.0.2.0/24"},
{ network = "198.51.100.0/24"},
{ network = "203.0.113.0/24"},
]
}
output "example_pool_size" {
value = format("pool '%s' is sized for %d addresses", apstra_ipv4_pool.example.name, apstra_ipv4_pool.example.total)
}
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
Initialise the backend again with Terraform Init
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % terraform init
Initializing the backend...
Migrating from Terraform Cloud to local state.
╷
│ Error: Migrating state from Terraform Cloud to another backend is not yet implemented.
│
│ Please use the API to do this: https://www.terraform.io/docs/cloud/api/state-versions.html
│
│
╵
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
There is an error Migrating state from Terraform Cloud to another backend is not yet implemented. But you get the idea of local and remote state storage.
Delete Workspace
There are two independent steps for destroying this workspace and any infrastructure associated with it. First, any Terraform infrastructure should be destroyed. Second, the workspace in Terraform Cloud, including any variables, settings, and alert history can be deleted.
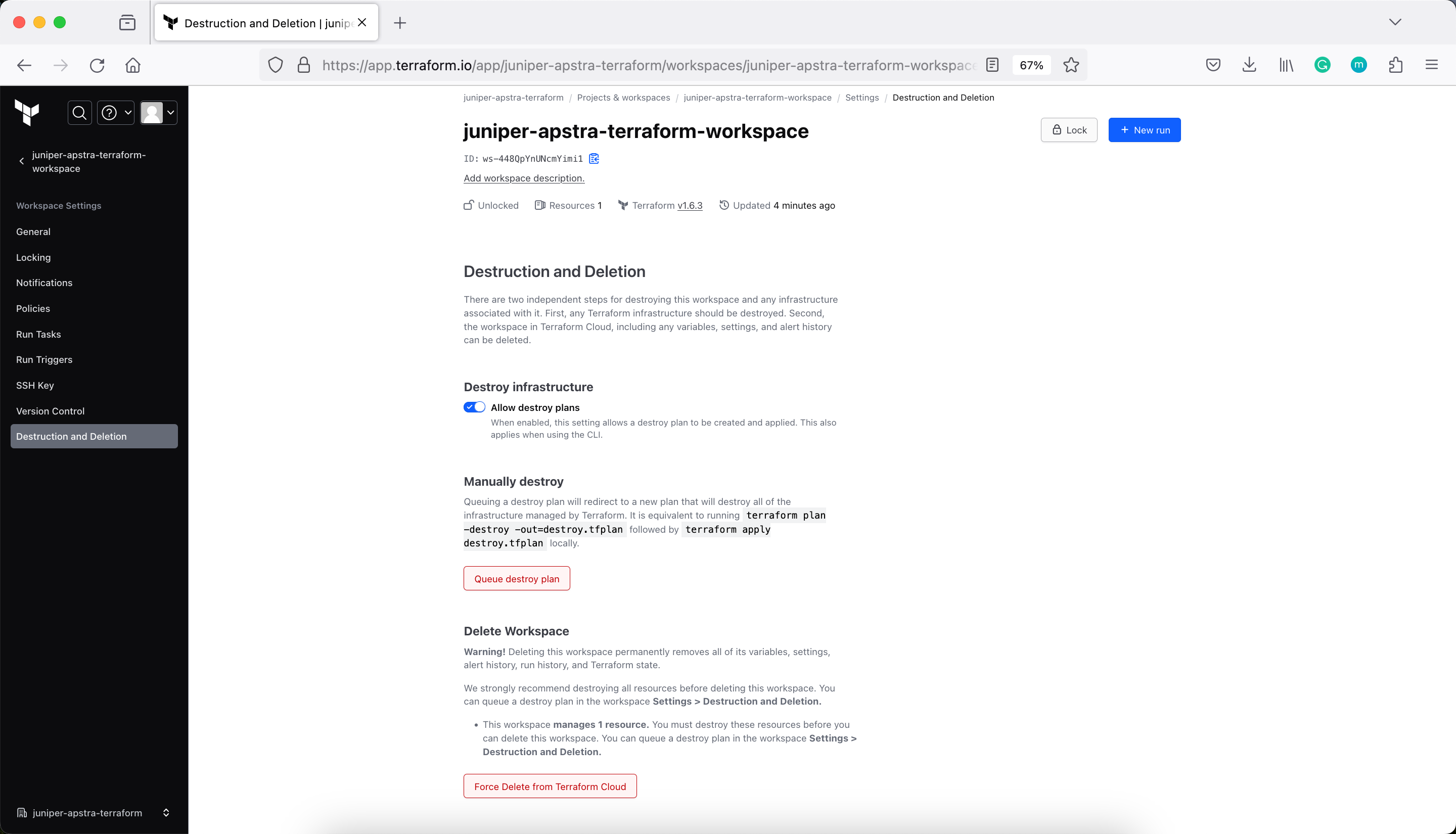
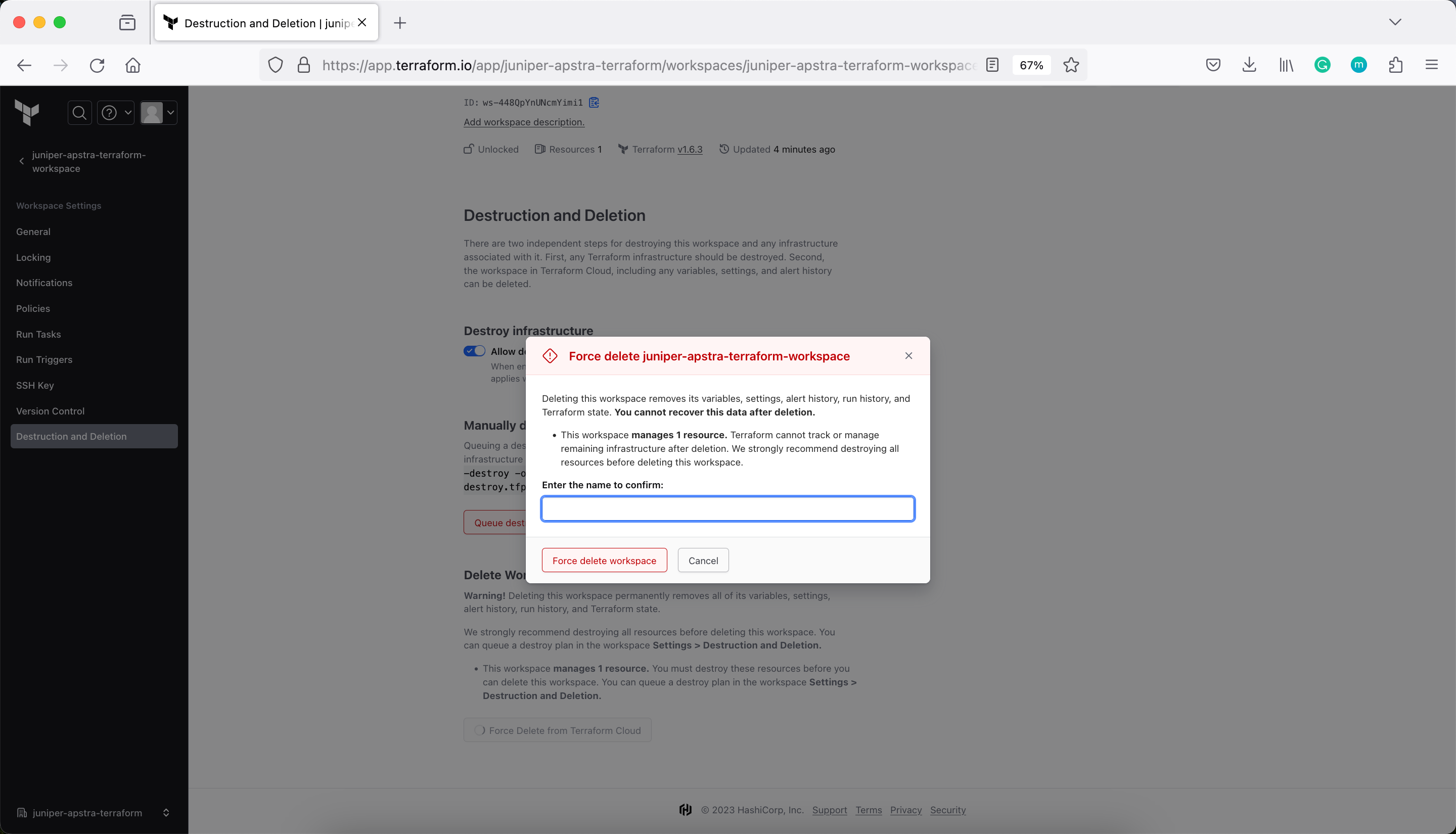
Verify the current Terraform state
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % terraform show
╷
│ Error: Backend initialization required, please run "terraform init"
│
│ Reason: Unsetting the previously set backend "cloud"
│
│ The "backend" is the interface that Terraform uses to store state,
│ perform operations, etc. If this message is showing up, it means that the
│ Terraform configuration you're using is using a custom configuration for
│ the Terraform backend.
│
│ Changes to backend configurations require reinitialization. This allows
│ Terraform to set up the new configuration, copy existing state, etc. Please run
│ "terraform init" with either the "-reconfigure" or "-migrate-state" flags to
│ use the current configuration.
│
│ If the change reason above is incorrect, please verify your configuration
│ hasn't changed and try again. At this point, no changes to your existing
│ configuration or state have been made.
╵
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
Migrate State
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % terraform init -migrate-state
Initializing the backend...
╷
│ Error: Invalid command-line option
│
│ The -migrate-state option is for migration between state backends only, and is not applicable when using Terraform Cloud.
│
│ Terraform Cloud migration has additional steps, configured by interactive prompts.
╵
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
Reconfigure
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 % terraform init -reconfigure
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Reusing previous version of juniper/apstra from the dependency lock file
- Using previously-installed juniper/apstra v0.42.0
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform-4 %
This concludes the getting started tutorials for Terraform. Now you can use Terraform to create and manage your infrastructure using Juniper Apstra.



