Creating Azure Resources with Terraform
Creating Azure Resource Group with Terraform
In this post, let us create a Terraform configuration to deploy an Azure resource group.
Authenticate using the Azure CLI
Terraform must authenticate to Azure to create infrastructure.
In your terminal, use the Azure CLI tool to setup your account permissions locally.
(base) pradeep:~$az login
A web browser has been opened at https://login.microsoftonline.com/organizations/oauth2/v2.0/authorize. Please continue the login in the web browser. If no web browser is available or if the web browser fails to open, use device code flow with `az login --use-device-code`.
[
{
"cloudName": "AzureCloud",
"homeTenantId": "xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxx",
"id": "xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx",
"isDefault": true,
"managedByTenants": [],
"name": "Pradeep",
"state": "Enabled",
"tenantId": "xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxx",
"user": {
"name": "gaddepradeep@gmail.com",
"type": "user"
}
}
]
(base) pradeep:~$
Note the id column for the subscription account you want to use.
Once you have chosen the account subscription ID, set the account with the Azure CLI.
(base) pradeep:~$az account set --subscription xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx
(base) pradeep:~$
Next, create a Service Principal. A Service Principal is an application within Azure Active Directory with the authentication tokens Terraform needs to perform actions on your behalf. Update the
(base) pradeep:~$az ad sp create-for-rbac --role="Contributor" --scopes="/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx"
The underlying Active Directory Graph API will be replaced by Microsoft Graph API in a future version of Azure CLI. Please carefully review all breaking changes introduced during this migration: https://docs.microsoft.com/cli/azure/microsoft-graph-migration
Creating 'Contributor' role assignment under scope '/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx'
The output includes credentials that you must protect. Be sure that you do not include these credentials in your code or check the credentials into your source control. For more information, see https://aka.ms/azadsp-cli
{
"appId": "xxxxxx-xxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxx",
"displayName": "azure-cli-2022-xxxxxxxx",
"password": "xxxxxx~xxxxxx~xxxxx",
"tenant": "xxxxx-xxxx-xxxxx-xxxx-xxxxx"
}
(base) pradeep:~$
In your terminal, set the following environment variables. Be sure to update the variable values with the values Azure returned in the previous command.
(base) pradeep:~$ export ARM_CLIENT_ID="<APPID_VALUE>"
(base) pradeep:~$ export ARM_CLIENT_SECRET="<PASSWORD_VALUE>"
(base) pradeep:~$ export ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID="<SUBSCRIPTION_ID>"
(base) pradeep:~$ export ARM_TENANT_ID="<TENANT_VALUE>"
Create a directory called learn-terraform-azure and Change into the new directory.
(base) pradeep:~$mkdir learn-terraform-azure
(base) pradeep:~$cd learn-terraform-azure
(base) pradeep:~
(base) pradeep:~$cat main.tf
# Configure the Azure provider
terraform {
required_providers {
azurerm = {
source = "hashicorp/azurerm"
version = "~> 3.0.2"
}
}
required_version = ">= 1.1.0"
}
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" {
name = "myTFResourceGroup"
location = "westus2"
}
(base) pradeep:~$
Initialize your learn-terraform-azure directory in your terminal.
(base) pradeep:~$terraform init
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Reusing previous version of hashicorp/azurerm from the dependency lock file
╷
│ Error: Failed to query available provider packages
│
│ Could not retrieve the list of available versions for provider hashicorp/azurerm: locked provider registry.terraform.io/hashicorp/azurerm 2.80.0 does not match configured version constraint ~> 3.0.2;
│ must use terraform init -upgrade to allow selection of new versions
╵
(base) pradeep:~$
Since I have tried this earlier with an old version of the Azure Provider, there is a mismatch between the locked provider and the required provider.
As shown in the error message, let us initilize again, this time with teh -upgrade option.
(base) pradeep:~$terraform init -upgrade
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Finding hashicorp/azurerm versions matching "~> 3.0.2"...
- Installing hashicorp/azurerm v3.0.2...
- Installed hashicorp/azurerm v3.0.2 (signed by HashiCorp)
Terraform has made some changes to the provider dependency selections recorded
in the .terraform.lock.hcl file. Review those changes and commit them to your
version control system if they represent changes you intended to make.
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
(base) pradeep:~$
Try running terraform plan
(base) pradeep:~$terraform plan
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# azurerm_resource_group.rg will be created
+ resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ location = "westus2"
+ name = "myTFResourceGroup"
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Note: You didn't use the -out option to save this plan, so Terraform can't guarantee to take exactly these actions if you run "terraform apply" now.
(base) pradeep:~$
(base) pradeep:~$terraform fmt
(base) pradeep:~$
(base) pradeep:~$terraform validate
Success! The configuration is valid.
(base) pradeep:~$
Apply your Terraform Configuration
Run the terraform apply command to apply your configuration.
(base) pradeep:~$terraform apply
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# azurerm_resource_group.rg will be created
+ resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ location = "westus2"
+ name = "myTFResourceGroup"
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
azurerm_resource_group.rg: Creating...
azurerm_resource_group.rg: Creation complete after 7s [id=/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx/resourceGroups/myTFResourceGroup]
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
(base) pradeep:~$
Navigate to the Azure portal in your web browser to validate the resource group.
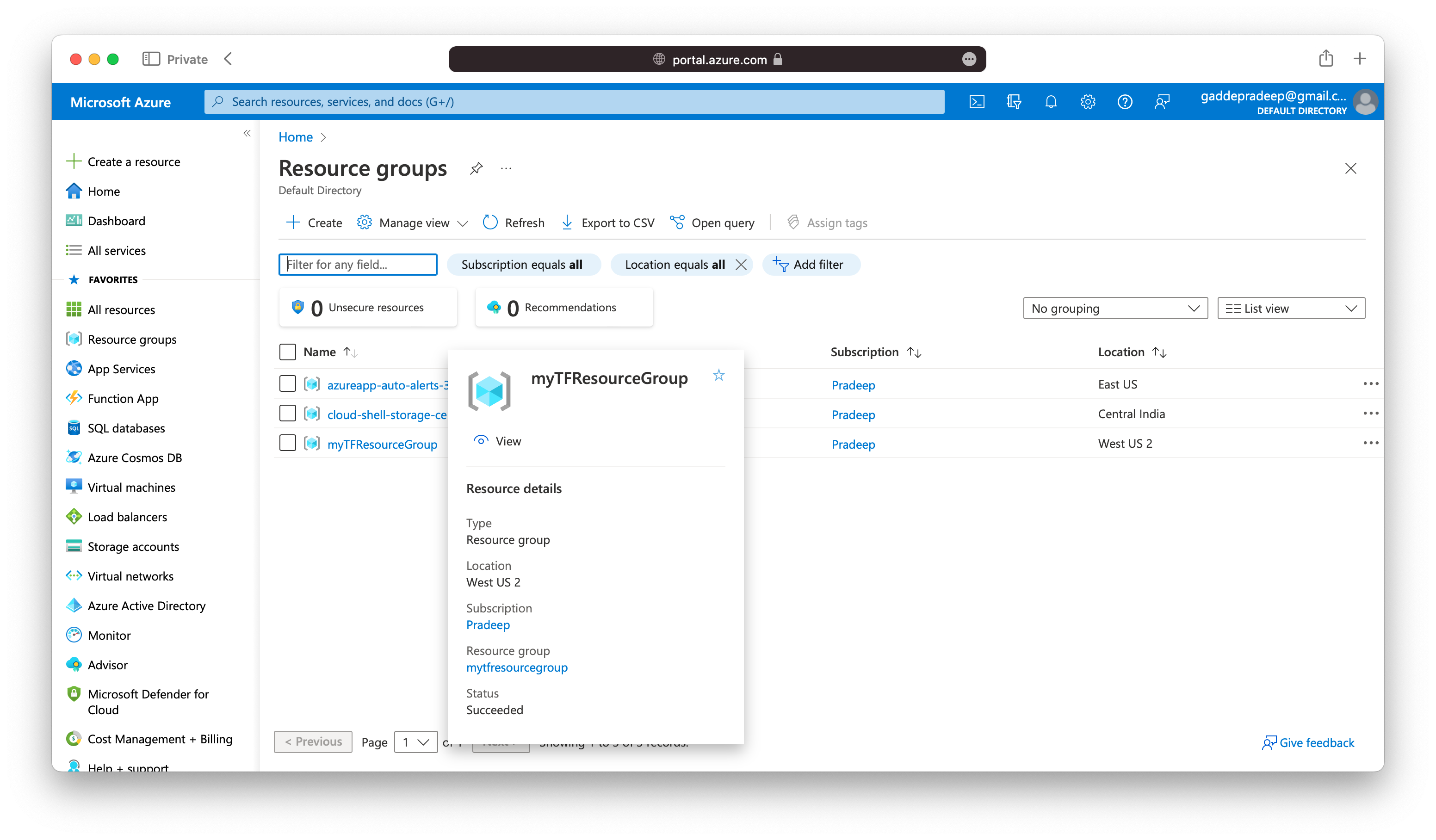
(base) pradeep:~$terraform show
# azurerm_resource_group.rg:
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" {
id = "/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx/resourceGroups/myTFResourceGroup"
location = "westus2"
name = "myTFResourceGroup"
}
(base) pradeep:~$
When Terraform created this resource group, it also gathered the resource’s properties and meta-data. These values can be referenced to configure other resources or outputs, which you will encounter in later tutorials.
To review the information in your state file, use the state command. If you have a long state file, you can see a list of the resources you created with Terraform by using the list subcommand.
(base) pradeep:~$terraform state list
azurerm_resource_group.rg
(base) pradeep:~$
(base) pradeep:~$terraform state
Usage: terraform [global options] state <subcommand> [options] [args]
This command has subcommands for advanced state management.
These subcommands can be used to slice and dice the Terraform state.
This is sometimes necessary in advanced cases. For your safety, all
state management commands that modify the state create a timestamped
backup of the state prior to making modifications.
The structure and output of the commands is specifically tailored to work
well with the common Unix utilities such as grep, awk, etc. We recommend
using those tools to perform more advanced state tasks.
Subcommands:
list List resources in the state
mv Move an item in the state
pull Pull current state and output to stdout
push Update remote state from a local state file
replace-provider Replace provider in the state
rm Remove instances from the state
show Show a resource in the state
(base) pradeep:~$
(base) pradeep:~$terraform state show azurerm_resource_group.rg
# azurerm_resource_group.rg:
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" {
id = "/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx/resourceGroups/myTFResourceGroup"
location = "westus2"
name = "myTFResourceGroup"
}
(base) pradeep:~$
This concludes our first post on creating Azure resources using Terraform.



