Azure Container Instances and Azure Kubernetes Service
If you want to run multiple instances of an application on a single host machine, containers are an excellent choice.
Unlike virtual machines, you don’t manage the operating system for a container. Virtual machines appear to be an instance of an operating system that you can connect to and manage, but containers are lightweight and designed to be created, scaled out, and stopped dynamically.
Containers are managed through a container orchestrator, which can start, stop, and scale out application instances as needed.
There are two ways to manage both Docker and Microsoft-based containers in Azure:
Azure Container Instances and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
Azure Container Instances
Fastest and simplest way to run a container in Azure. It’s a platform as a service (PaaS) offering that allows you to upload your containers, which it runs for you.
Azure Container Instances (ACI) allows you to quickly and easily run containers on Azure without managing servers or having to learn new tools. ACI offers per-second billing to minimize the cost of running containers on the cloud.
Azure Kubernetes Service
Azure Kubernetes Service is a complete orchestration service for containers with distributed architectures and large volumes of containers.
You might ask, what is Orchestration? The task of automating, managing, and interacting with a large number of containers is known as orchestration.
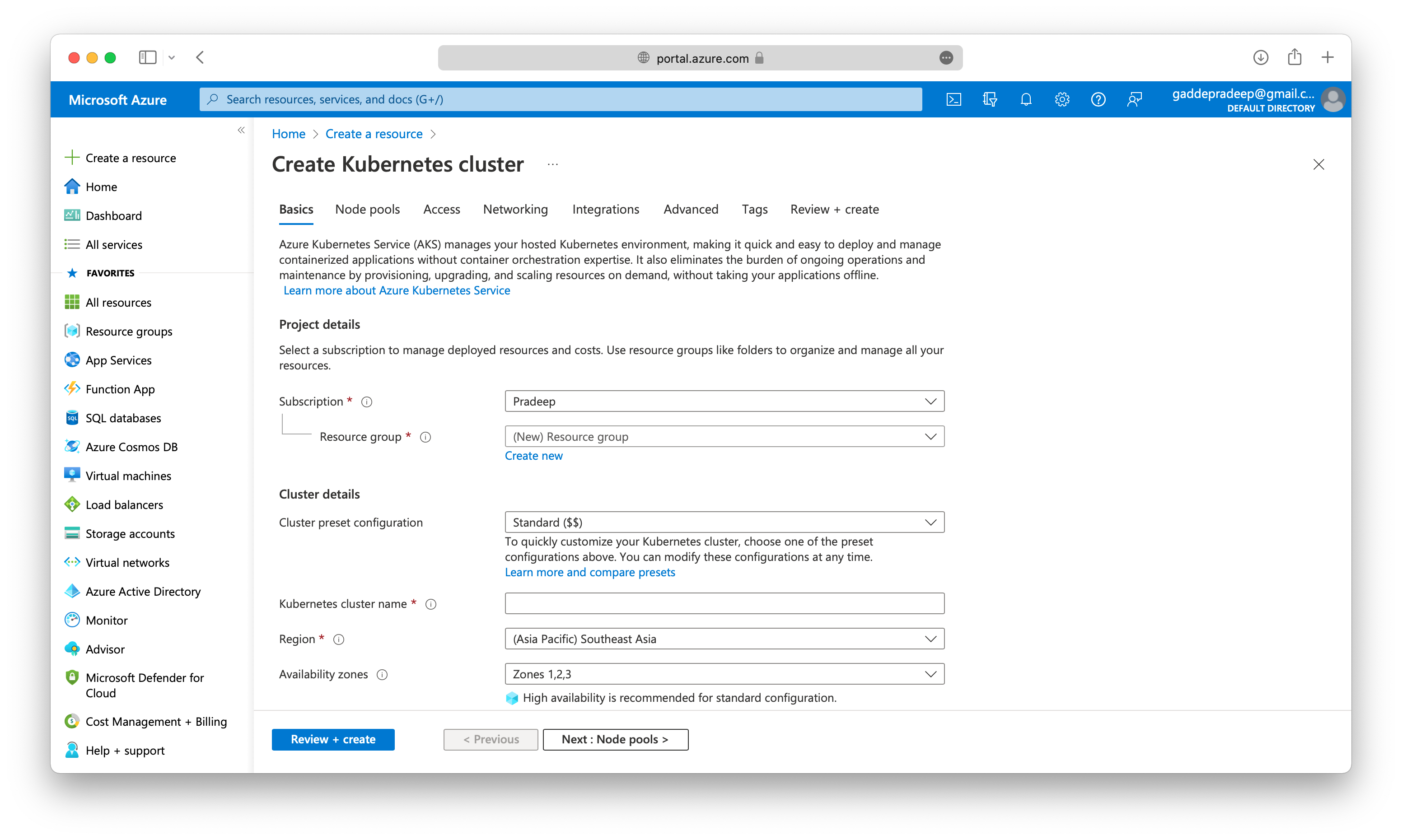
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) manages your hosted Kubernetes environment, making it quick and easy to deploy and manage containerized applications without container orchestration expertise. It also eliminates the burden of ongoing operations and maintenance by provisioning, upgrading, and scaling resources on demand, without taking your applications offline.
Micro Service Architecture
Containers are often used to create solutions by using a microservice architecture. This architecture is where you break solutions into smaller, independent pieces.
For example, you might split a website into
- a container hosting your front end,
- another hosting your back end, and
- a third for storage.
This split allows you to separate portions of your app into logical sections that can be maintained, scaled, or updated independently.
Here is a screenshot of creating Container resources in Azure.
and here is how we create AKS (Kubernetes Clusters)