Cloud Computing Models
Cloud Computing Models
There are three cloud models:
- Public Cloud: services offered over internet, no capex, pay for what you use
- Private Cloud: for one specific organization (internal use), complete control, hardware maintenance
- Hybrid Cloud: Combined use of Public and Private Clouds, more flexible
Cloud Computing Advantages
- High Availability
- Scalability
- Elasticity
- Agility
- Geo Distribution
- Disaster Recovery
CapEx vs OpEx
CapEx requires significant up-front financial costs, as well as ongoing maintenance and support expenditures. By contrast, OpEx is a consumption-based model.
Cloud service providers operate on a consumption-based model, which means that end users only pay for the resources that they use. Whatever they use is what they pay for. A consumption-based model has many benefits, including:
- No upfront costs.
- No need to purchase and manage costly infrastructure that users might not use to its fullest.
- The ability to pay for additional resources when they are needed.
- The ability to stop paying for resources that are no longer needed.
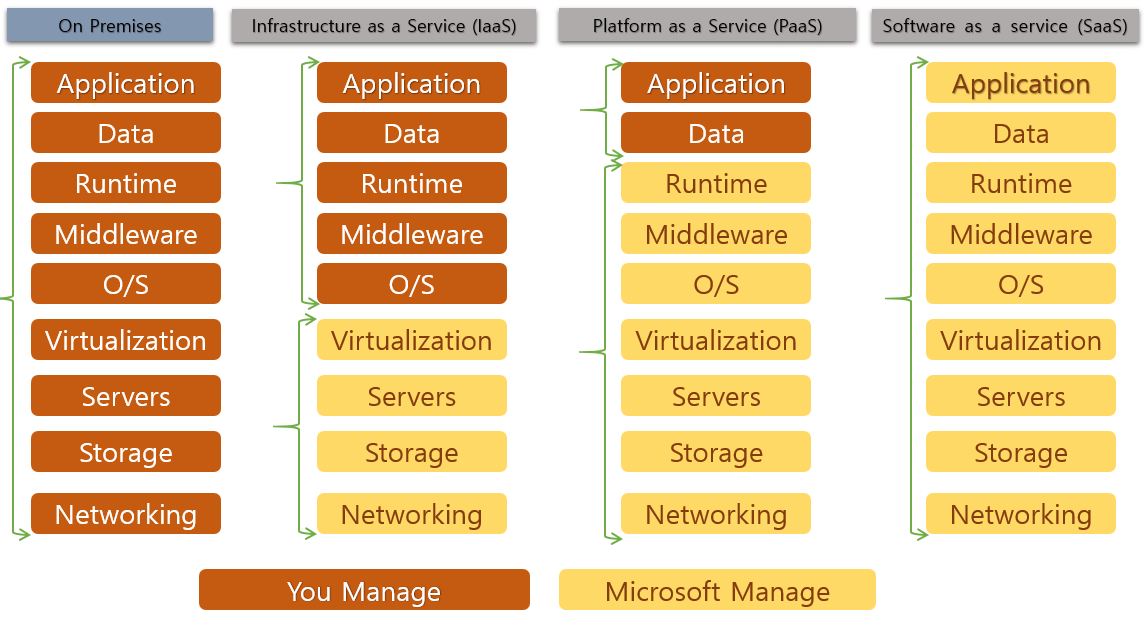
Cloud Service Models
-
IaaS Infrastructure-as-a-Service
-
PaaS Platform-as-a-Service
-
SaaS Software-as-a-Service
The following diagram from Microsoft summarizes the three cloud service models.
Serverless
Serverless computing is similar to PaaS. Serverless architectures are highly scalable and event-driven, only using resources when a specific function or trigger occurs. Though the name says server less, there is a server running the applications, it is just that they are managed by the Cloud provider.



