Getting Started with Juniper Apstra Terraform Provider
Getting Started with Juniper Apstra Terraform Provider
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools, such as Terraform, allow you to manage infrastructure with configuration files rather than through a graphical user interface (like Juniper Apstra Web UI). IaC allows you to build, change, and manage your infrastructure in a safe, consistent, and repeatable way by defining resource configurations that you can version, reuse, and share.
Terraform plugins called providers let Terraform interact with cloud platforms and other services such as Juniper Apstra via their application programming interfaces (APIs). HashiCorp and the Terraform community have written over 1,000 providers to manage resources on various cloud providers.
Juniper Apstra also released a Terraform Provider https://registry.terraform.io/providers/Juniper/apstra/latest
The Apstra provider allows Terraform to control Juniper Apstra fabrics.
It covers day 0 and day 1 operations (design and deployment), and a growing list of day 2 capabilities.
Providers define individual units of infrastructure, for example compute instances or private networks as resources. You can compose resources from different providers into reusable Terraform configurations called modules, and manage them with a consistent language and workflow.
Terraform’s configuration language (HCL) is declarative, meaning that it describes the desired end-state for your infrastructure, in contrast to procedural programming languages that require step-by-step instructions to perform tasks. Terraform providers automatically calculate dependencies between resources to create or destroy them in the correct order.
Install Terraform
If you have installed Terraform sometime ago, probably it is best to install the latest version.
First check the current version of Terraform.
pradeep@juniper ~ % terraform version
Terraform v1.5.3
on darwin_amd64
Your version of Terraform is out of date! The latest version
is 1.6.3. You can update by downloading from https://www.terraform.io/downloads.html
pradeep@juniper ~ % which terraform
/usr/local/bin/terraform
Download the latest Terraform from https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/install
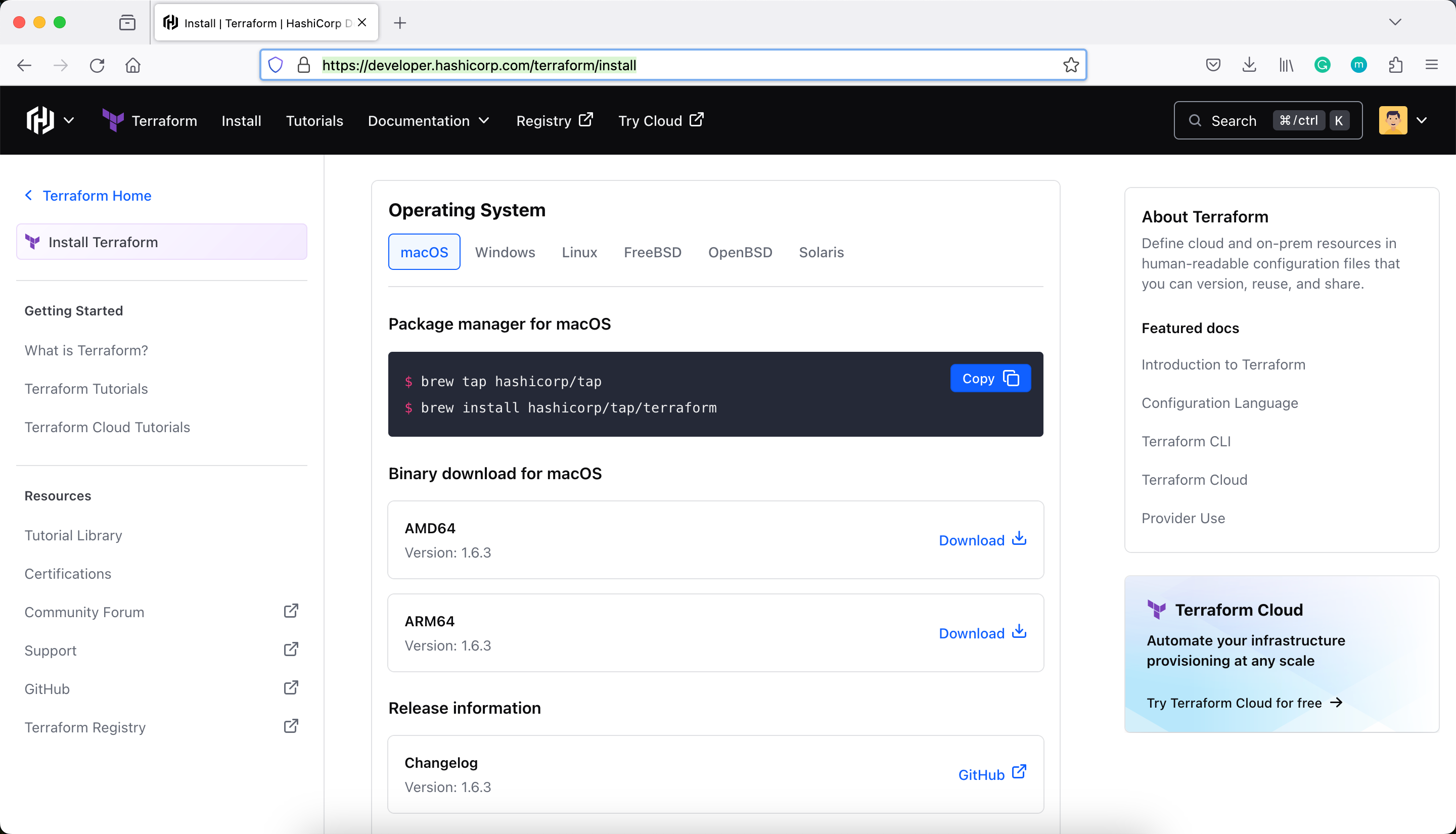
pradeep@juniper ~ % mv Downloads/terraform /usr/local/bin/terraform
override r-xr-xr-x pradga/admin for /usr/local/bin/terraform? (y/n [n]) y
pradeep@juniper ~ % terraform version
Terraform v1.6.3
on darwin_amd64
pradeep@juniper ~ %
Install Juniper Apstra
Add the Juniper Apstra AOS Server Node and a Management network.
aos-server login: admin
Password:
You are required to change your password immediately (root enforced)
Changing password for admin.
(current) UNIX password:
New password:
Retype new password:
Last login: Tue Jan 10 04:52:17 UTC 2023 from 10.0.2.2 on pts/0
Apstra Operating System (AOS) Virtual Appliance
Copyright (C) 2014-2023, Apstra Inc.
All rights reserved.
Support: https://support.juniper.net/
Version: 4.1.2-269
Access the Web UI.
Login using the credentials setup during the initial install.
Install Apstra Terraform Provider
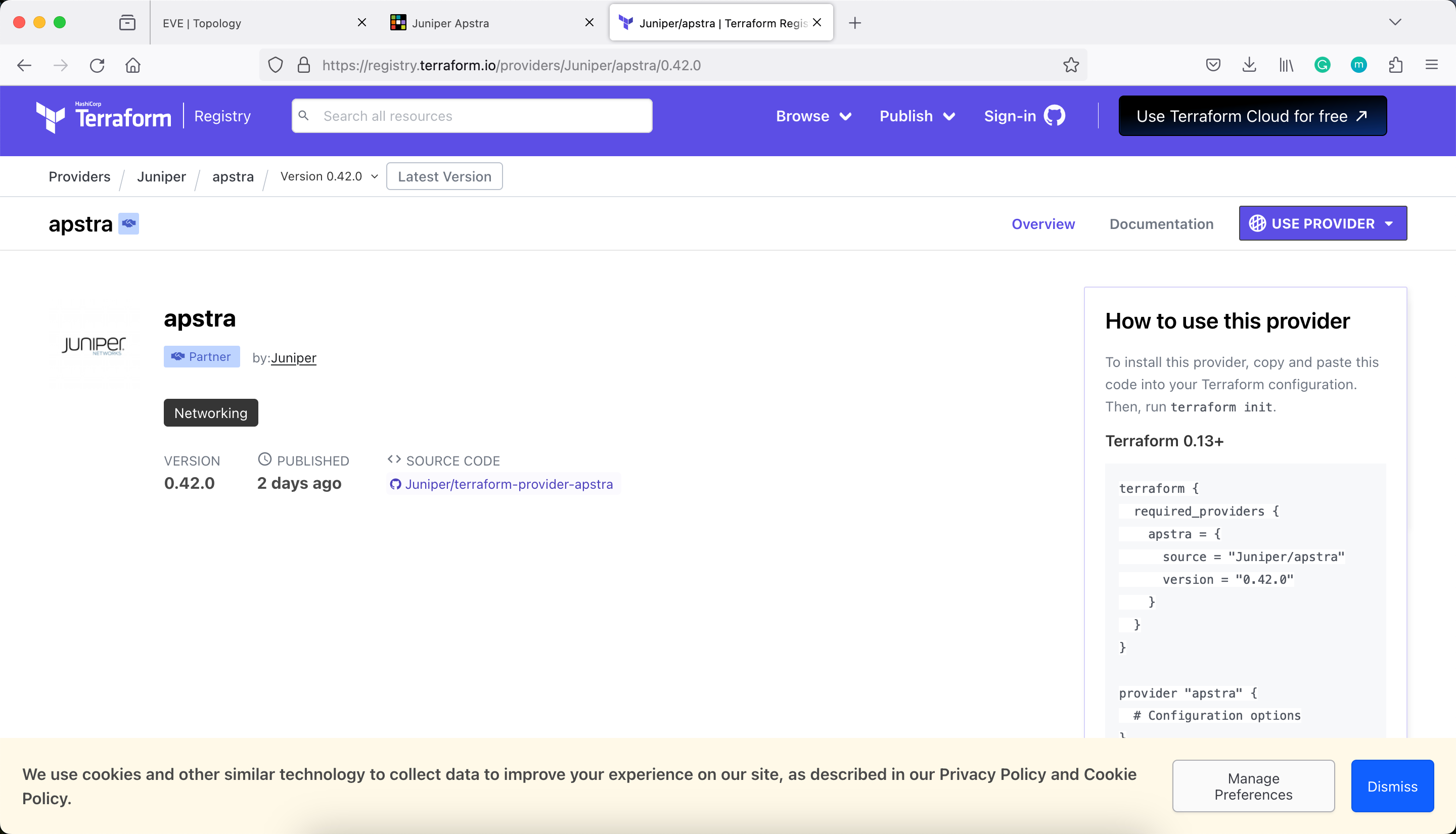
Refer to the https://github.com/Juniper/terraform-provider-apstra/tree/main/lab_guide_demo
pradeep@juniper ~ % mkdir apstra-terraform
pradeep@juniper ~ % cd apstra-terraform
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % vi 0_provider.tf
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % cat 0_provider.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
apstra = {
source = "Juniper/apstra"
version = "0.42.0"
}
}
}
provider "apstra" {
# URL and credentials can be supplied using the "url" parameter in this file.
url = "https://<username>:<password>@<hostname-or-ip-address>:<port>"
#
# ...or using the environment variable APSTRA_URL.
#
# If Username or Password are not embedded in the URL, the provider will look
# for them in the APSTRA_USER and APSTRA_PASS environment variables.
#
tls_validation_disabled = true
}
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform %
Initialize
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % terraform init
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Finding juniper/apstra versions matching "0.42.0"...
- Installing juniper/apstra v0.42.0...
- Installed juniper/apstra v0.42.0 (signed by a HashiCorp partner, key ID CB9C922903A66F3F)
Partner and community providers are signed by their developers.
If you'd like to know more about provider signing, you can read about it here:
https://www.terraform.io/docs/cli/plugins/signing.html
Terraform has created a lock file .terraform.lock.hcl to record the provider
selections it made above. Include this file in your version control repository
so that Terraform can guarantee to make the same selections by default when
you run "terraform init" in the future.
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform %
Create a Resource
Let’s start with a simple Juniper Apstra resource, that is an ASN pool.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % vi 1_resources.tf
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % cat 1_resources.tf
resource "apstra_asn_pool" "rfc5398" {
name = "RFC5398 ASNs"
ranges = [
{
first = 64496
last = 64511
},
{
first = 65536
last = 65551
},
]
}
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform %
Plan
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % terraform plan
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# apstra_asn_pool.rfc5398 will be created
+ resource "apstra_asn_pool" "rfc5398" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = "RFC5398 ASNs"
+ ranges = [
+ {
+ first = 64496
+ last = 64511
+ status = (known after apply)
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
},
+ {
+ first = 65536
+ last = 65551
+ status = (known after apply)
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
},
]
+ status = (known after apply)
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
╷
│ Warning: Possibly unsafe default - No exclusive Blueprint access
│
│ with provider["registry.terraform.io/juniper/apstra"],
│ on 0_provider.tf line 13, in provider "apstra":
│ 13: provider "apstra" {
│
│ The provider's 'blueprint_mutex_enabled' configuration attribute is not set. This attribute is used to explicitly opt-in to, or opt-out of, signaling exclusive Blueprint access via a mutex. The default
│ behavior (false) does not use a mutex, and is appropriate for learning, development environments, and anywhere there's no risk of multiple automation systems attempting to make changes within a single
│ Blueprint at the same time.
│
│ Set `blueprint_mutex_enabled` to either `true` or `false` to suppresss this warning.
╵
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Note: You didn't use the -out option to save this plan, so Terraform can't guarantee to take exactly these actions if you run "terraform apply" now.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform %
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % cat 0_provider.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
apstra = {
source = "Juniper/apstra"
version = "0.42.0"
}
}
}
provider "apstra" {
# URL and credentials can be supplied using the "url" parameter in this file.
url = "https://<username>:<password>@<hostname-or-ip-address>:<port>"
#
# ...or using the environment variable APSTRA_URL.
#
# If Username or Password are not embedded in the URL, the provider will look
# for them in the APSTRA_USER and APSTRA_PASS environment variables.
#
tls_validation_disabled = true
blueprint_mutex_enabled = true
}
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform %
Check the plan again, now that you have enabled mutex.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % terraform plan
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# apstra_asn_pool.rfc5398 will be created
+ resource "apstra_asn_pool" "rfc5398" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = "RFC5398 ASNs"
+ ranges = [
+ {
+ first = 64496
+ last = 64511
+ status = (known after apply)
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
},
+ {
+ first = 65536
+ last = 65551
+ status = (known after apply)
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
},
]
+ status = (known after apply)
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Note: You didn't use the -out option to save this plan, so Terraform can't guarantee to take exactly these actions if you run "terraform apply" now.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform %
Save the Plan
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % terraform plan -out=apstra-asn-pool-create
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# apstra_asn_pool.rfc5398 will be created
+ resource "apstra_asn_pool" "rfc5398" {
+ id = (known after apply)
+ name = "RFC5398 ASNs"
+ ranges = [
+ {
+ first = 64496
+ last = 64511
+ status = (known after apply)
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
},
+ {
+ first = 65536
+ last = 65551
+ status = (known after apply)
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
},
]
+ status = (known after apply)
+ total = (known after apply)
+ used = (known after apply)
+ used_percentage = (known after apply)
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Saved the plan to: apstra-asn-pool-create
To perform exactly these actions, run the following command to apply:
terraform apply "apstra-asn-pool-create"
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform %
Apply the Plan
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % terraform apply apstra-asn-pool-create
apstra_asn_pool.rfc5398: Creating...
apstra_asn_pool.rfc5398: Creation complete after 2s [id=33638076-17d5-4981-9b00-800f4afc0529]
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform %
Verify that the ASN pool, named RFC5398 ASNs is created in Juniper Apstra.
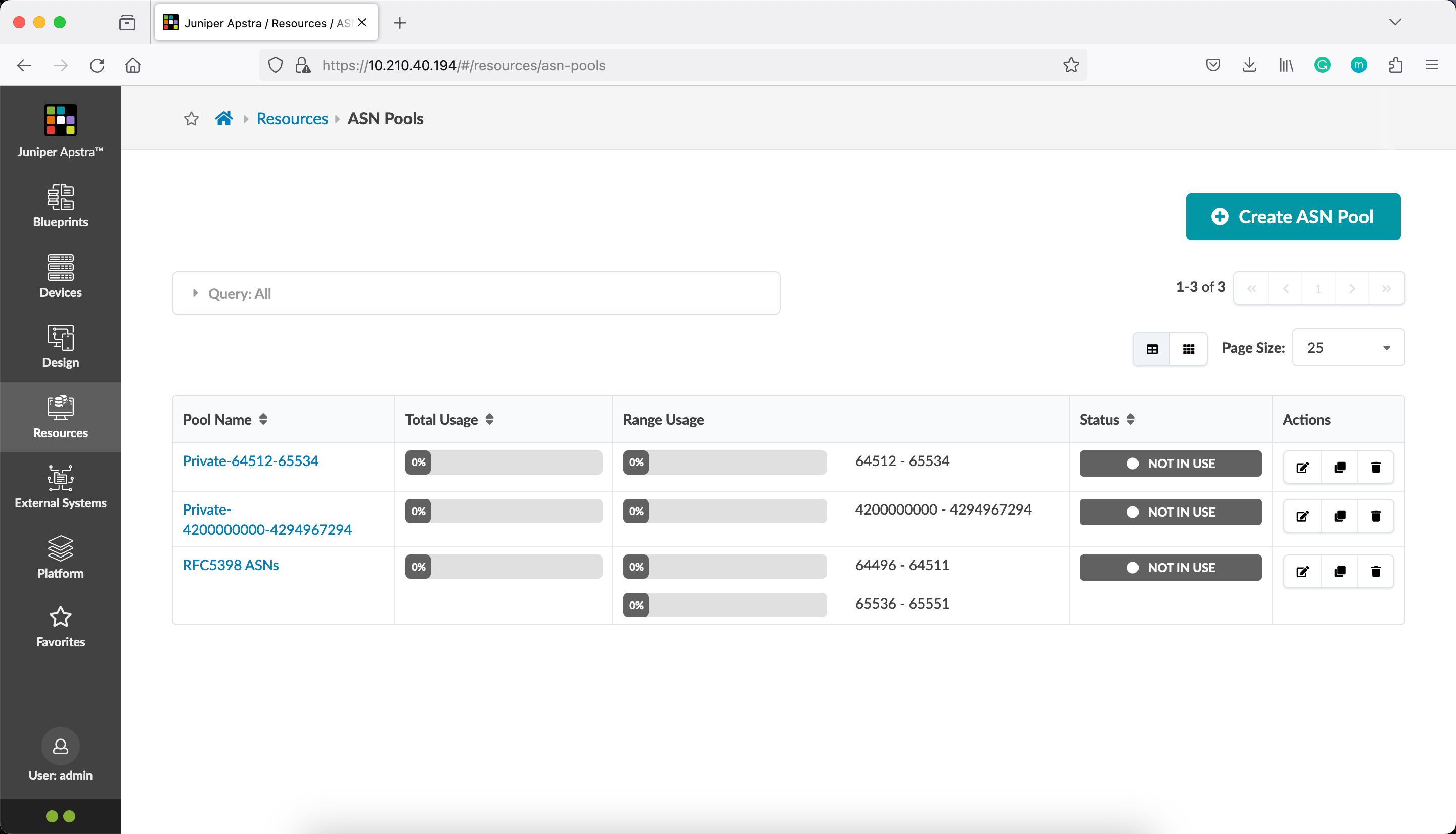
We can see that along with the default pools, we have the third pool, created using Juniper Apstra Terraform Provider.
Congratulations! You have successfully created a Juniper Apstra resource using Terraform now.
Verify the Terraform State
Terraform keeps track of your real infrastructure in a state file, which acts as a source of truth for your environment. Terraform uses the state file (terraform.tfstate) to determine the changes to make to your infrastructure so that it will match your configuration.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % terraform show
# apstra_asn_pool.rfc5398:
resource "apstra_asn_pool" "rfc5398" {
id = "33638076-17d5-4981-9b00-800f4afc0529"
name = "RFC5398 ASNs"
ranges = [
{
first = 64496
last = 64511
status = "pool_element_available"
total = 16
used = 0
used_percentage = 0
},
{
first = 65536
last = 65551
status = "pool_element_available"
total = 16
used = 0
used_percentage = 0
},
]
status = "not_in_use"
total = 32
used = 0
used_percentage = 0
}
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform %
Other way to look at it is using terraform.tfstate.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % cat terraform.tfstate
{
"version": 4,
"terraform_version": "1.6.3",
"serial": 1,
"lineage": "4e17feac-09b7-e4ef-e51a-a490ae1bb0db",
"outputs": {},
"resources": [
{
"mode": "managed",
"type": "apstra_asn_pool",
"name": "rfc5398",
"provider": "provider[\"registry.terraform.io/juniper/apstra\"]",
"instances": [
{
"schema_version": 0,
"attributes": {
"id": "33638076-17d5-4981-9b00-800f4afc0529",
"name": "RFC5398 ASNs",
"ranges": [
{
"first": 64496,
"last": 64511,
"status": "pool_element_available",
"total": 16,
"used": 0,
"used_percentage": 0
},
{
"first": 65536,
"last": 65551,
"status": "pool_element_available",
"total": 16,
"used": 0,
"used_percentage": 0
}
],
"status": "not_in_use",
"total": 32,
"used": 0,
"used_percentage": 0
},
"sensitive_attributes": []
}
]
}
],
"check_results": null
}
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform %
Destroy Resources
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % terraform destroy
apstra_asn_pool.rfc5398: Refreshing state... [id=33638076-17d5-4981-9b00-800f4afc0529]
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols:
- destroy
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# apstra_asn_pool.rfc5398 will be destroyed
- resource "apstra_asn_pool" "rfc5398" {
- id = "33638076-17d5-4981-9b00-800f4afc0529" -> null
- name = "RFC5398 ASNs" -> null
- ranges = [
- {
- first = 64496 -> null
- last = 64511 -> null
- status = "pool_element_available" -> null
- total = 16 -> null
- used = 0 -> null
- used_percentage = 0 -> null
},
- {
- first = 65536 -> null
- last = 65551 -> null
- status = "pool_element_available" -> null
- total = 16 -> null
- used = 0 -> null
- used_percentage = 0 -> null
},
] -> null
- status = "not_in_use" -> null
- total = 32 -> null
- used = 0 -> null
- used_percentage = 0 -> null
}
Plan: 0 to add, 0 to change, 1 to destroy.
Do you really want to destroy all resources?
Terraform will destroy all your managed infrastructure, as shown above.
There is no undo. Only 'yes' will be accepted to confirm.
Enter a value: yes
apstra_asn_pool.rfc5398: Destroying... [id=33638076-17d5-4981-9b00-800f4afc0529]
apstra_asn_pool.rfc5398: Destruction complete after 1s
Destroy complete! Resources: 1 destroyed.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform %
Verify that the ASN pool resource (named RFC5398 ASNs) is removed from Juniper Apstra.
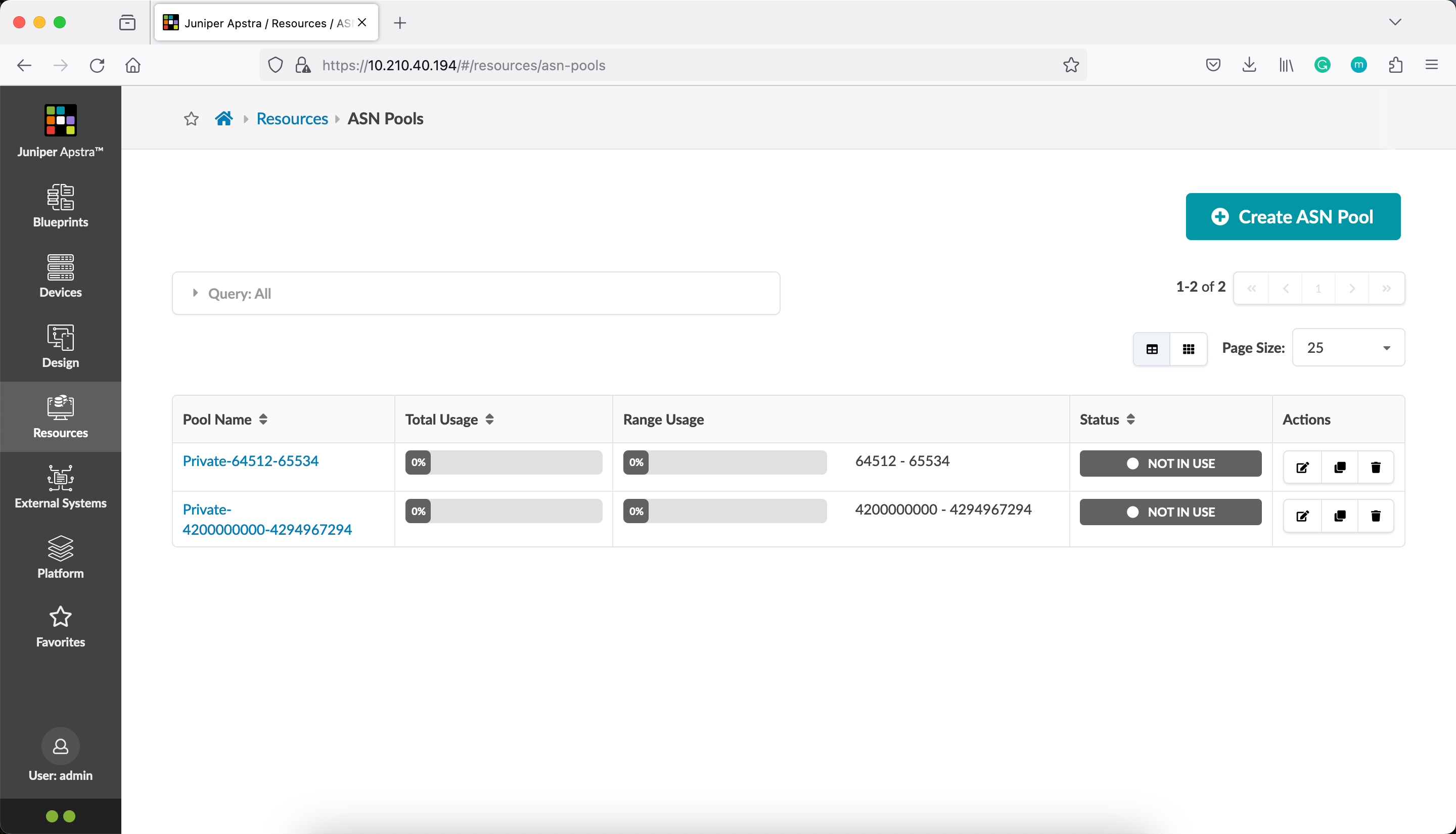
After destroying the resource, verify the Terraform state.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform % terraform show
The state file is empty. No resources are represented.
pradeep@juniper apstra-terraform %



