Getting Started with VPC Networking and Google Compute Engine
Google Cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) provides networking functionality to Compute Engine virtual machine (VM) instances, Kubernetes Engine containers, and App Engine flexible environment. In other words, without a VPC network you cannot create VM instances, containers, or App Engine applications. Therefore, each Google Cloud project has a default network to get you started.
You can think of a VPC network as similar to a physical network, except that it is virtualized within Google Cloud. A VPC network is a global resource that consists of a list of regional virtual subnetworks (subnets) in data centers, all connected by a global wide area network (WAN). VPC networks are logically isolated from each other in Google Cloud.
In this lab, you create an auto mode VPC network with firewall rules and two VM instances. Then, you explore the connectivity for the VM instances.
- Explore the default VPC network
- Create an auto mode network with firewall rules
- Create VM instances using Compute Engine
- Explore the connectivity for VM instances
1. Explore the default network
In the Cloud Console, on the Navigation menu (
Notice the default network with its subnets. Each subnet is associated with a Google Cloud region and a private RFC 1918 CIDR block for its internal IP addresses range and a gateway.
View the routes
Routes tell VM instances and the VPC network how to send traffic from an instance to a destination, either inside the network or outside Google Cloud. Each VPC network comes with some default routes to route traffic among its subnets and send traffic from eligible instances to the internet.
- In the left pane, click Routes. Notice that there is a route for each subnet and one for the Default internet gateway (0.0.0.0/0). These routes are managed for you, but you can create custom static routes to direct some packets to specific destinations. For example, you can create a route that sends all outbound traffic to an instance configured as a NAT gateway.
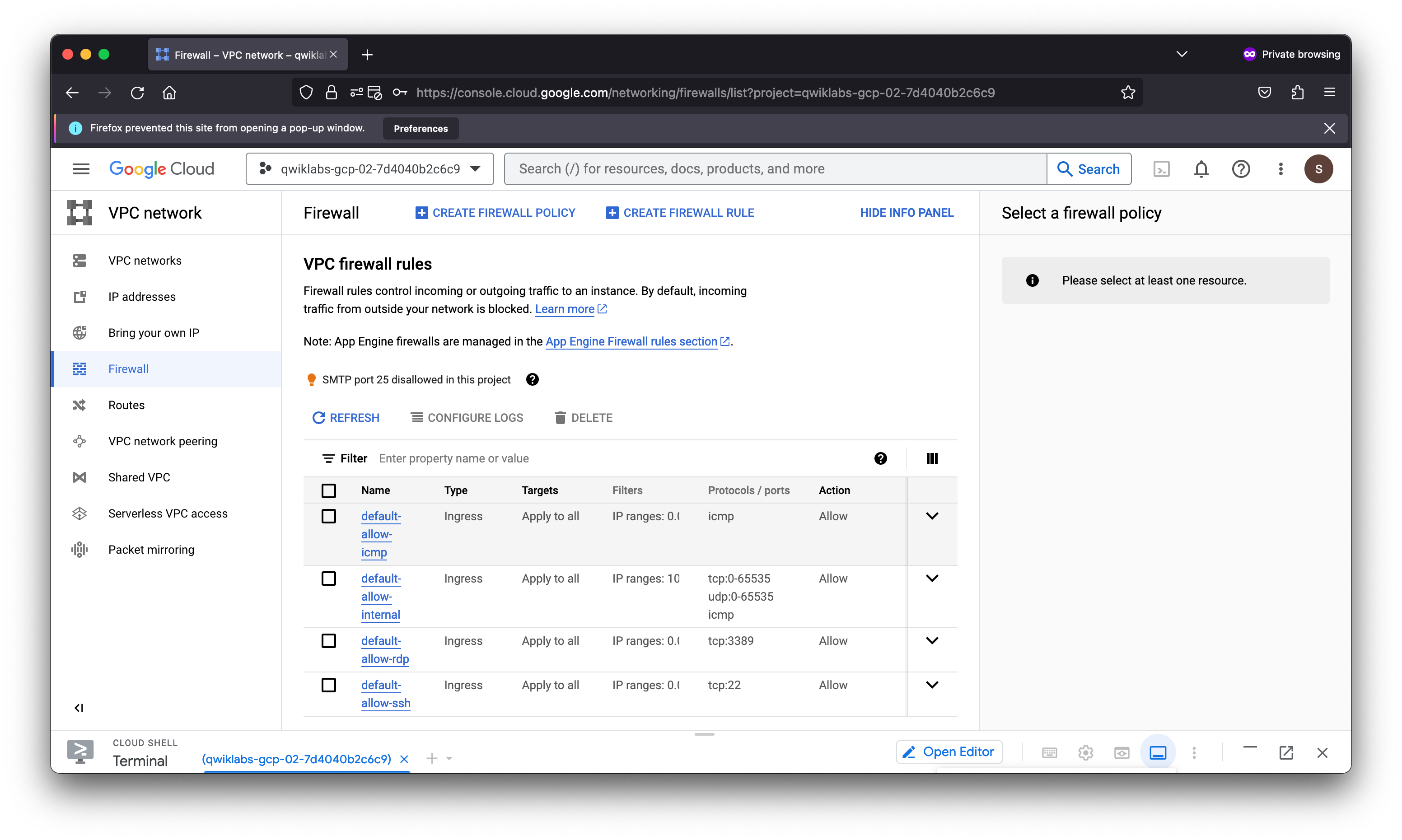
View the Firewall rules
Each VPC network implements a distributed virtual firewall that you can configure. Firewall rules allow you to control which packets are allowed to travel to which destinations. Every VPC network has two implied firewall rules that block all incoming connections and allow all outgoing connections.
-
In the left pane, click Firewall
Notice that there are 4 Ingress firewall rules for the default network:
- default-allow-icmp
- default-allow-rdp
- default-allow-ssh
- default-allow-internal
student_01_cd9de465be5c@cloudshell:~ (qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9)$ gcloud compute networks list
NAME: default
SUBNET_MODE: AUTO
BGP_ROUTING_MODE: REGIONAL
IPV4_RANGE:
GATEWAY_IPV4:
student_01_cd9de465be5c@cloudshell:~ (qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9)$
student_01_cd9de465be5c@cloudshell:~ (qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9)$ gcloud compute networks subnets list
NAME: default
REGION: us-central1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.128.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: europe-west1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.132.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: us-west1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.138.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: asia-east1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.140.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: us-east1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.142.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: asia-northeast1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.146.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: asia-southeast1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.148.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: us-east4
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.150.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: australia-southeast1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.152.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: europe-west2
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.154.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: europe-west3
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.156.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: asia-south1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.160.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: europe-west4
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.164.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: europe-north1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.166.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: us-west2
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.168.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: us-west3
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.180.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: us-west4
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.182.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: europe-central2
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.186.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: southamerica-west1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.194.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: us-east7
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.196.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: us-east5
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.202.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: us-south1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.206.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: me-west1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.208.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: europe-west12
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.210.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
NAME: default
REGION: me-central1
NETWORK: default
RANGE: 10.212.0.0/20
STACK_TYPE: IPV4_ONLY
IPV6_ACCESS_TYPE:
INTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
EXTERNAL_IPV6_PREFIX:
student_01_cd9de465be5c@cloudshell:~ (qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9)$
student_01_cd9de465be5c@cloudshell:~ (qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9)$ gcloud compute routes list
NAME: default-route-0629d5f8681a8921
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.196.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-0863b29d2ea5ff84
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.146.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-0e11a293ead13588
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 0.0.0.0/0
NEXT_HOP: default-internet-gateway
PRIORITY: 1000
NAME: default-route-14a76fdbae76c783
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.186.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-14bdd3aeadc23120
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.166.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-19ead2cbfc059dc9
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.206.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-257a63f57cd9523f
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.164.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-323e5a5fd35e600c
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.128.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-3e5814ba18762ea2
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.194.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-42051fb31d846694
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.140.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-7e9c78e563c7c74f
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.154.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-821257f9e85883f5
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.142.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-87d5a96dd7d9c11d
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.182.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-918de52ff414da99
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.156.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-a4ce6ea18ab527ae
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.160.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-a91fada5a89942f1
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.208.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-b62f6770963dc1ff
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.210.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-b7572191bb454fcf
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.168.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-b9aaefbe2a702e5a
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.148.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-c1fc55b72a4fc8cc
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.212.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-c65cb9d667f93b07
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.138.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-cdcc0b078f987059
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.180.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-d013ecf3e7167865
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.202.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-dd9fa8e48ed4d789
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.152.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-e77304a1d3123405
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.150.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
NAME: default-route-f7c98e9f95e6c3d8
NETWORK: default
DEST_RANGE: 10.132.0.0/20
NEXT_HOP: default
PRIORITY: 0
student_01_cd9de465be5c@cloudshell:~ (qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9)$
student_01_cd9de465be5c@cloudshell:~ (qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9)$ gcloud compute firewall-rules list
NAME: default-allow-icmp
NETWORK: default
DIRECTION: INGRESS
PRIORITY: 65534
ALLOW: icmp
DENY:
DISABLED: False
NAME: default-allow-internal
NETWORK: default
DIRECTION: INGRESS
PRIORITY: 65534
ALLOW: tcp:0-65535,udp:0-65535,icmp
DENY:
DISABLED: False
NAME: default-allow-rdp
NETWORK: default
DIRECTION: INGRESS
PRIORITY: 65534
ALLOW: tcp:3389
DENY:
DISABLED: False
NAME: default-allow-ssh
NETWORK: default
DIRECTION: INGRESS
PRIORITY: 65534
ALLOW: tcp:22
DENY:
DISABLED: False
To show all fields of the firewall, please show in JSON format: --format=json
To show all fields in table format, please see the examples in --help.
student_01_cd9de465be5c@cloudshell:~ (qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9)$
Try to create a VM instance
Verify that you cannot create a VM instance without a VPC network.
- On the Navigation menu (
), click Compute Engine > VM instances.
- Click Create instance.
- Accept the default values and click Create. Notice the error.
- Click Management, security, disks, networking, sole tenancy.
- Click Networking. Notice the No local network available error under Network interfaces.
- Click Cancel.
2. Create a VPC network and VM instances
Create a VPC network so that you can create VM instances.
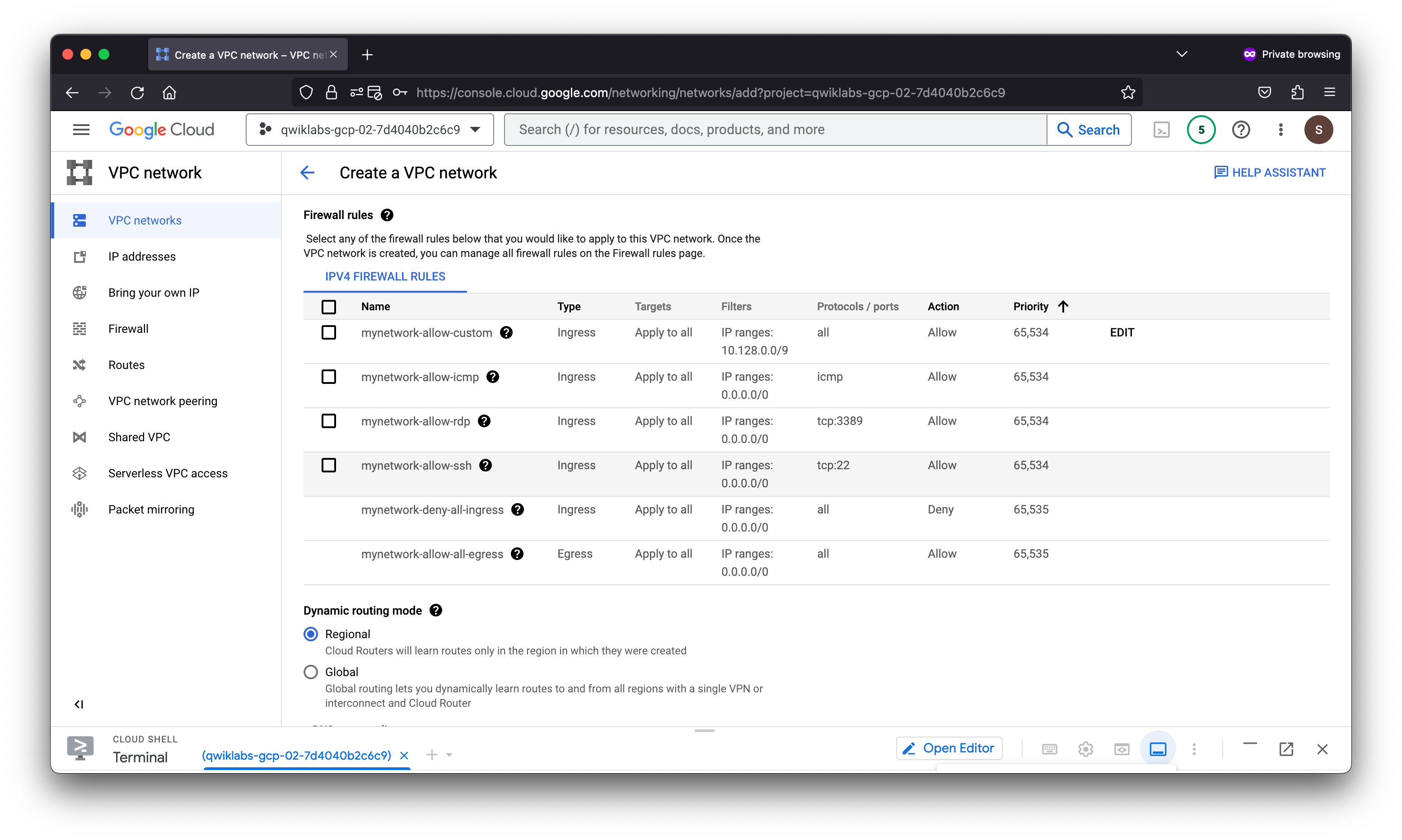
Create an auto mode VPC network with Firewall rules
gcloud compute networks create mynetwork --project=qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9 --subnet-mode=auto --mtu=1460 --bgp-routing-mode=regional
gcloud compute firewall-rules create mynetwork-allow-custom --project=qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9 --network=projects/qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9/global/networks/mynetwork --description=Allows\ connection\ from\ any\ source\ to\ any\ instance\ on\ the\ network\ using\ custom\ protocols. --direction=INGRESS --priority=65534 --source-ranges=10.128.0.0/9 --action=ALLOW --rules=all
gcloud compute firewall-rules create mynetwork-allow-icmp --project=qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9 --network=projects/qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9/global/networks/mynetwork --description=Allows\ ICMP\ connections\ from\ any\ source\ to\ any\ instance\ on\ the\ network. --direction=INGRESS --priority=65534 --source-ranges=0.0.0.0/0 --action=ALLOW --rules=icmp
gcloud compute firewall-rules create mynetwork-allow-rdp --project=qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9 --network=projects/qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9/global/networks/mynetwork --description=Allows\ RDP\ connections\ from\ any\ source\ to\ any\ instance\ on\ the\ network\ using\ port\ 3389. --direction=INGRESS --priority=65534 --source-ranges=0.0.0.0/0 --action=ALLOW --rules=tcp:3389
gcloud compute firewall-rules create mynetwork-allow-ssh --project=qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9 --network=projects/qwiklabs-gcp-02-7d4040b2c6c9/global/networks/mynetwork --description=Allows\ TCP\ connections\ from\ any\ source\ to\ any\ instance\ on\ the\ network\ using\ port\ 22. --direction=INGRESS --priority=65534 --source-ranges=0.0.0.0/0 --action=ALLOW --rules=tcp:22
Create a VM instance in us-central1
Create a VM instance in the region. Selecting a region and zone determines the subnet and assigns the internal IP address from the subnet’s IP address range.
Create a VM instance in europe-west2
Create a VM instance in the europe-west2 region.
3. Explore the connectivity for VM instances
Explore the connectivity for the VM instances. Specifically, try to SSH to your VM instances using tcp:22, and ping both the internal and external IP addresses of your VM instances using ICMP. Then explore the effects of the firewall rules on connectivity by removing the firewall rules individually.
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
Creating directory '/home/student-01-cd9de465be5c'.
student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$ ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1460 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 42:01:0a:80:00:02 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
altname enp0s4
inet 10.128.0.2/32 brd 10.128.0.2 scope global dynamic ens4
valid_lft 3343sec preferred_lft 3343sec
inet6 fe80::4001:aff:fe80:2/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$
student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$ ping 10.154.0.2 -c 3
PING 10.154.0.2 (10.154.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.154.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=94.9 ms
64 bytes from 10.154.0.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=94.6 ms
64 bytes from 10.154.0.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=94.6 ms
--- 10.154.0.2 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2003ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 94.586/94.693/94.907/0.151 ms
student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$ ip route
default via 10.128.0.1 dev ens4
10.128.0.1 dev ens4 scope link
student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$
You can ping mynet-eu-vm’s internal IP because of the allow-custom firewall rule.
student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$ ping 35.189.124.113 -c 3
PING 35.189.124.113 (35.189.124.113) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 35.189.124.113: icmp_seq=1 ttl=52 time=97.2 ms
64 bytes from 35.189.124.113: icmp_seq=2 ttl=52 time=95.5 ms
64 bytes from 35.189.124.113: icmp_seq=3 ttl=52 time=95.5 ms
--- 35.189.124.113 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2003ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 95.478/96.055/97.193/0.804 ms
student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$
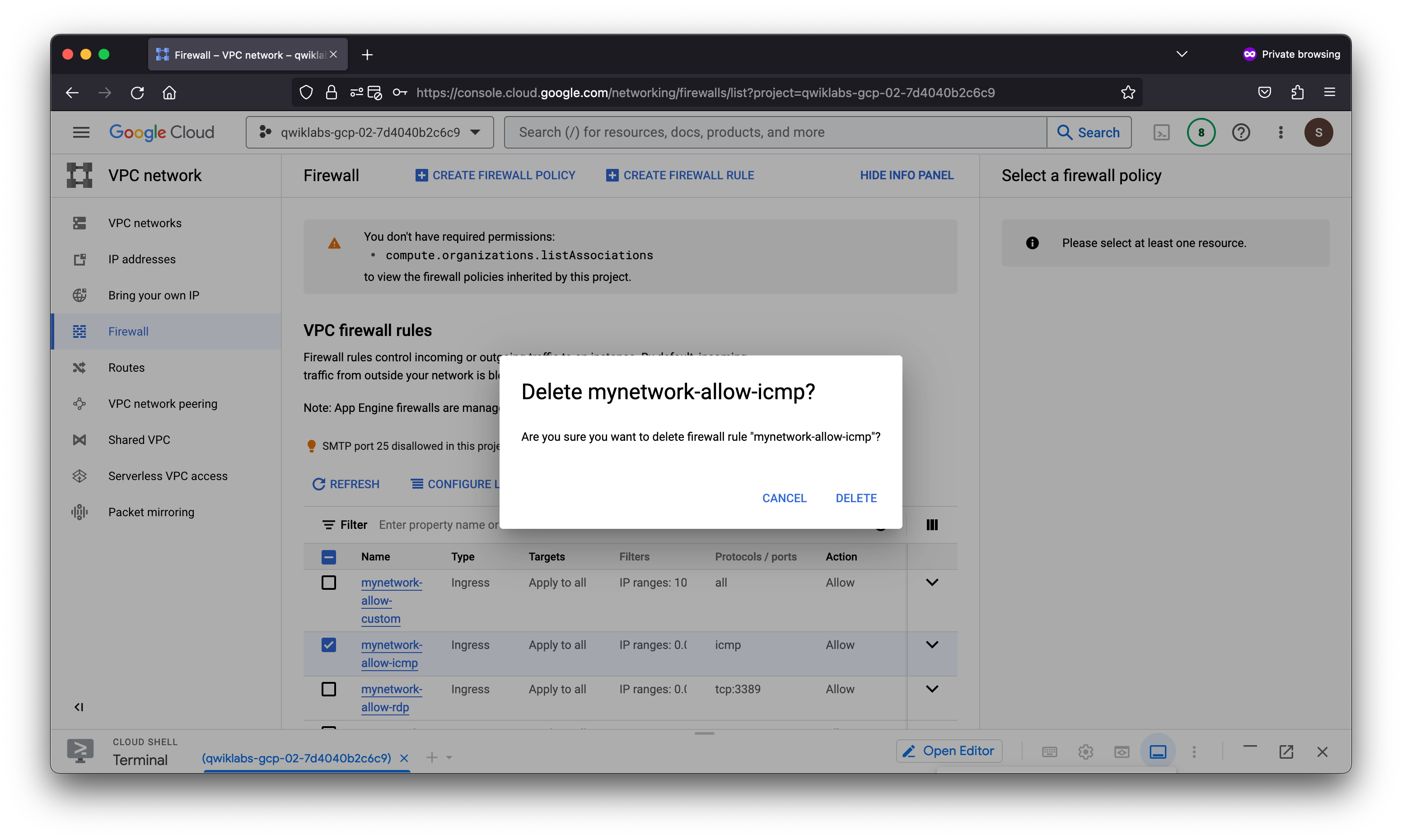
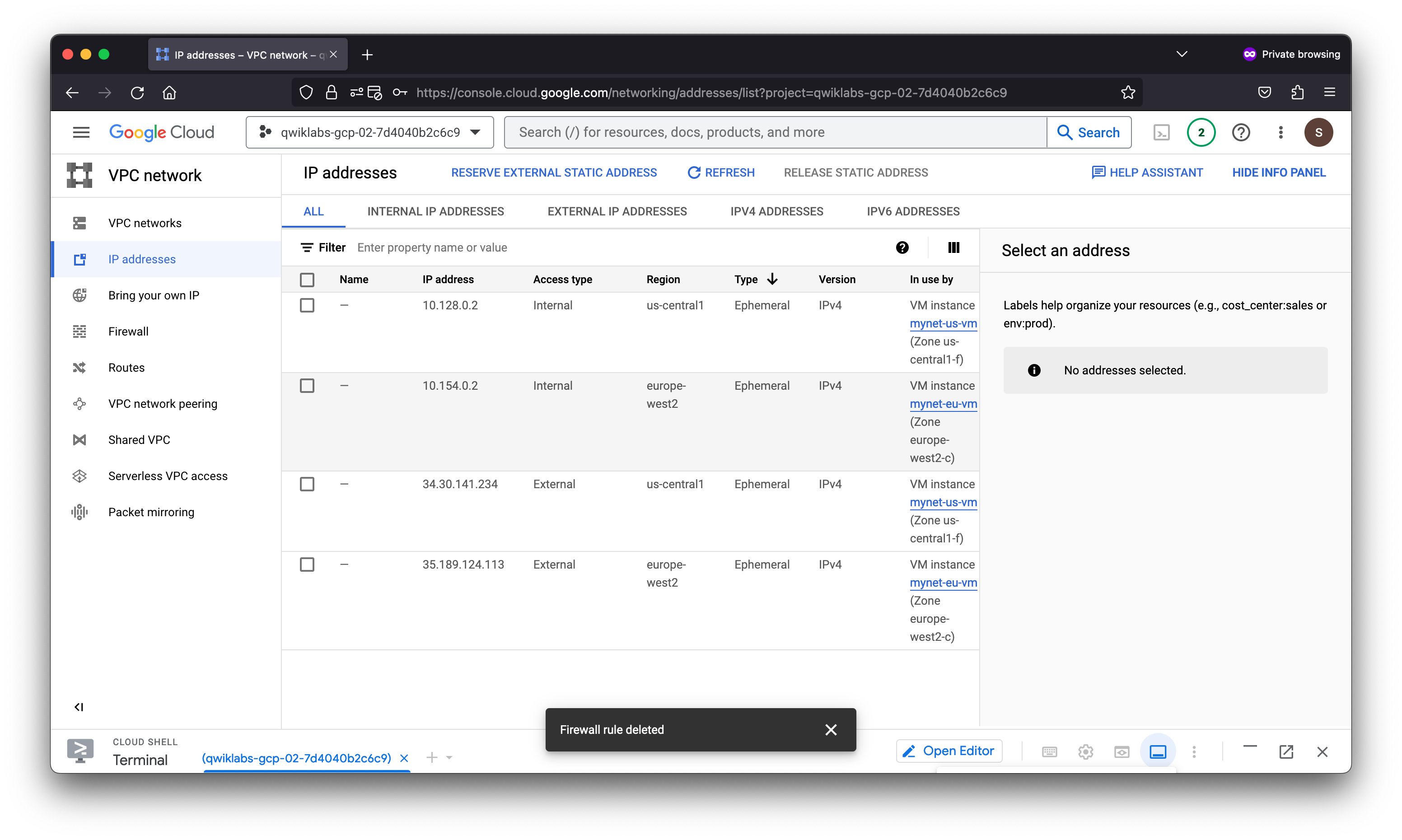
Remove the allow-icmp firewall rules
Remove the allow-icmp firewall rule and try to ping the internal and external IP address of mynet-eu-vm.
- On the Navigation menu (
), click VPC network > Firewall.
- Select the mynetwork-allow-icmp rule.
- Click Delete.
- Click Delete to confirm the deletion. Wait for the firewall rule to be deleted.
- Return to the mynet-us-vm SSH terminal.
student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$ ping 10.154.0.2 -c 3
PING 10.154.0.2 (10.154.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.154.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=94.8 ms
64 bytes from 10.154.0.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=93.7 ms
64 bytes from 10.154.0.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=93.7 ms
--- 10.154.0.2 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2003ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 93.690/94.074/94.789/0.506 ms
student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$ ping 35.189.124.113 -c 3
PING 35.189.124.113 (35.189.124.113) 56(84) bytes of data.
--- 35.189.124.113 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 2025ms
student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$
You can ping mynet-eu-vm’s internal IP because of the allow-custom firewall rule
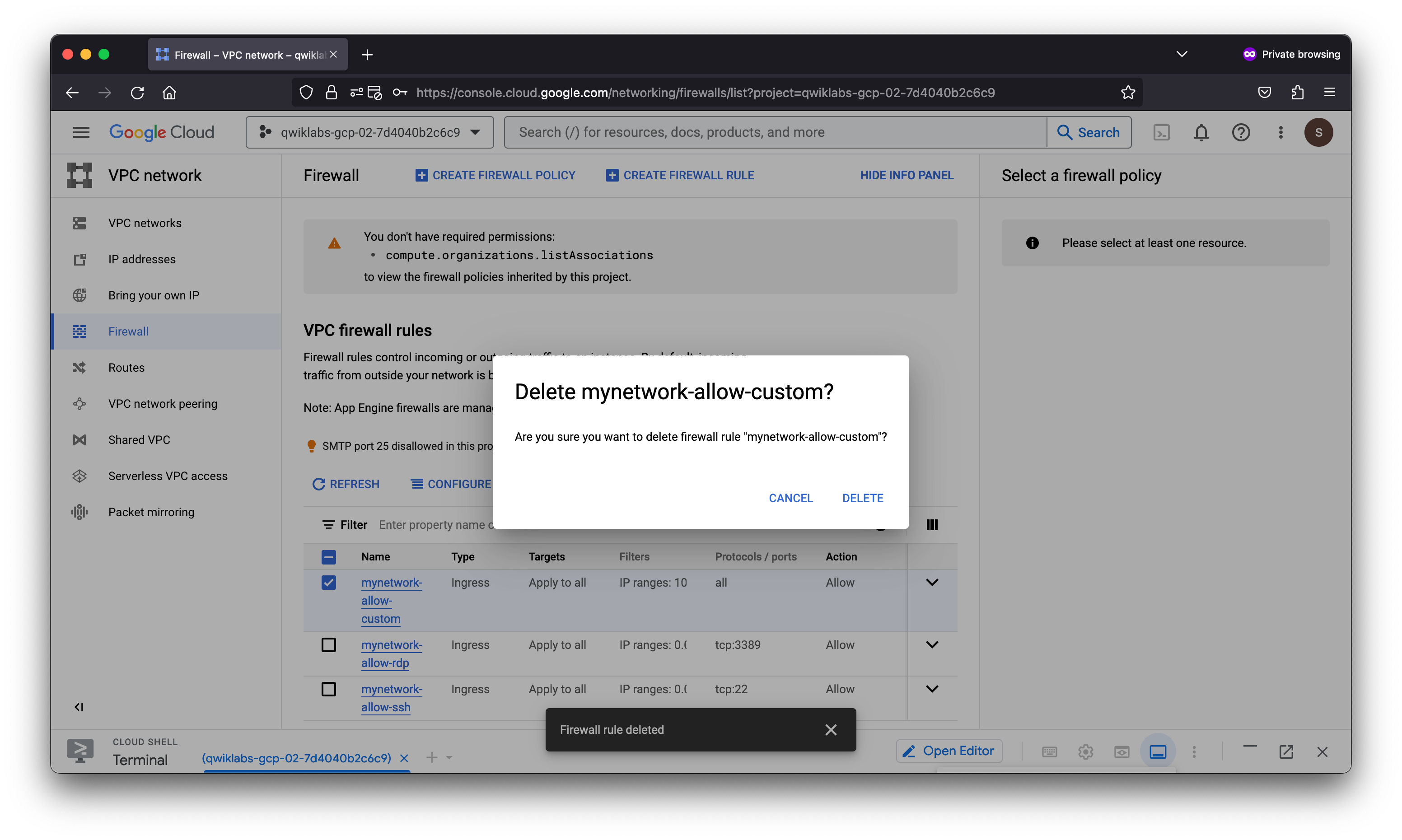
Remove the allow-custom firewall rules
Remove the allow-custom firewall rule and try to ping the internal IP address of mynet-eu-vm.
-
On the Navigation menu (
), click VPC network > Firewall.
-
Select the mynetwork-allow-custom rule.
-
Click Delete.
-
Click Delete to confirm the deletion. Wait for the firewall rule to be deleted.
-
Return to the mynet-us-vm SSH terminal.
student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$ ping 10.154.0.2 -c 3 PING 10.154.0.2 (10.154.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data. --- 10.154.0.2 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 2027ms student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$ ping 35.189.124.113 -c 3 PING 35.189.124.113 (35.189.124.113) 56(84) bytes of data. --- 35.189.124.113 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 0 received, 100% packet loss, time 2030ms student-01-cd9de465be5c@mynet-us-vm:~$
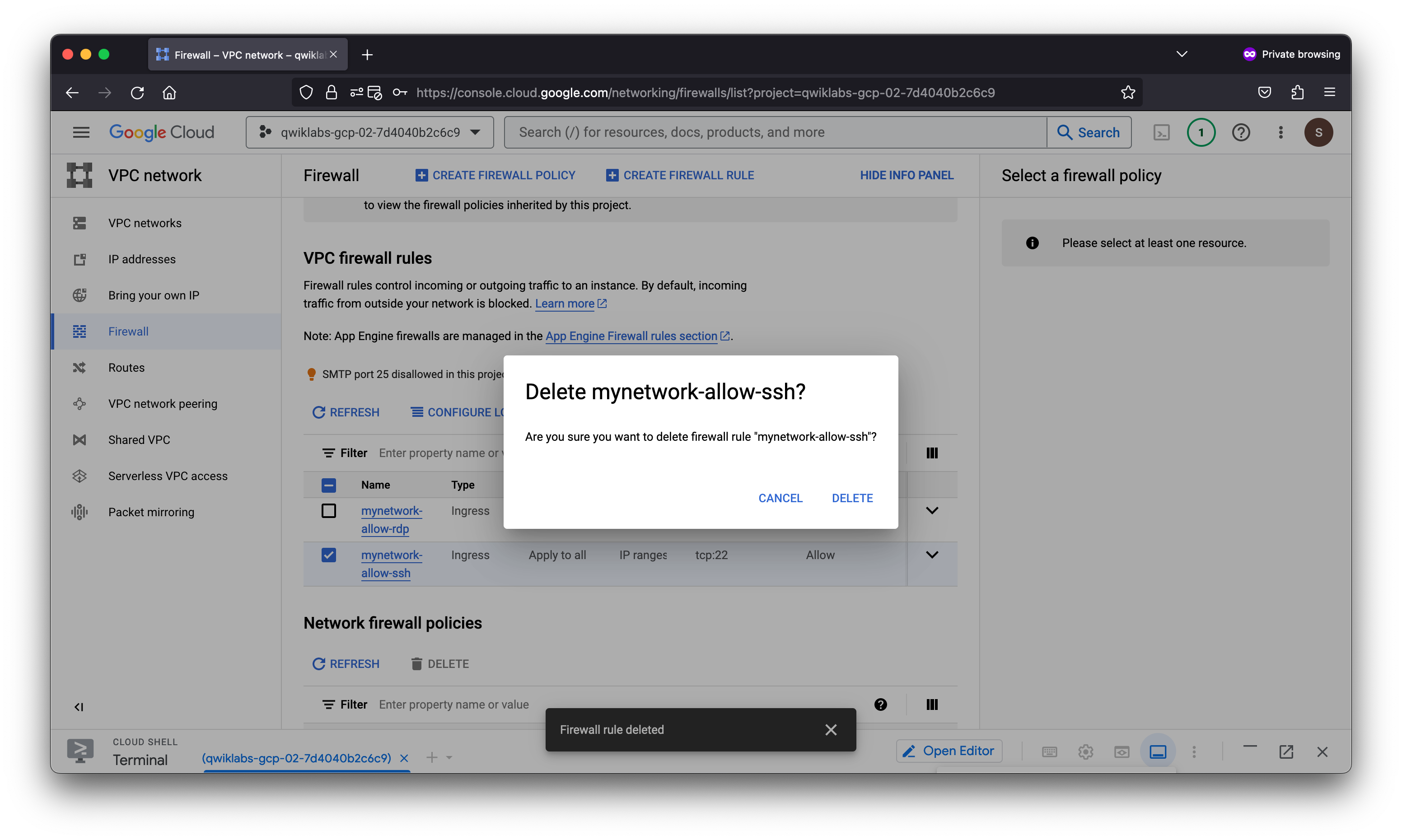
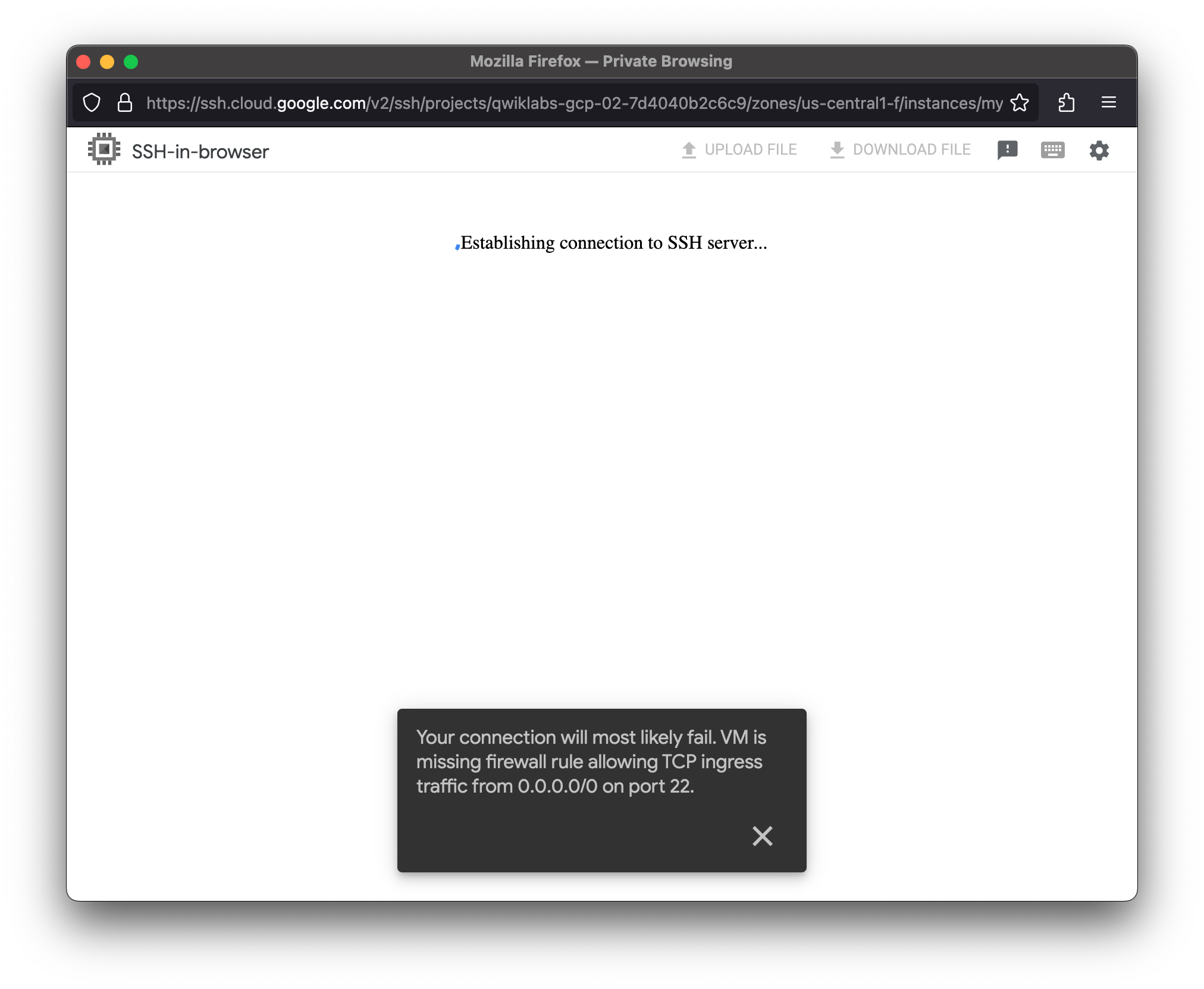
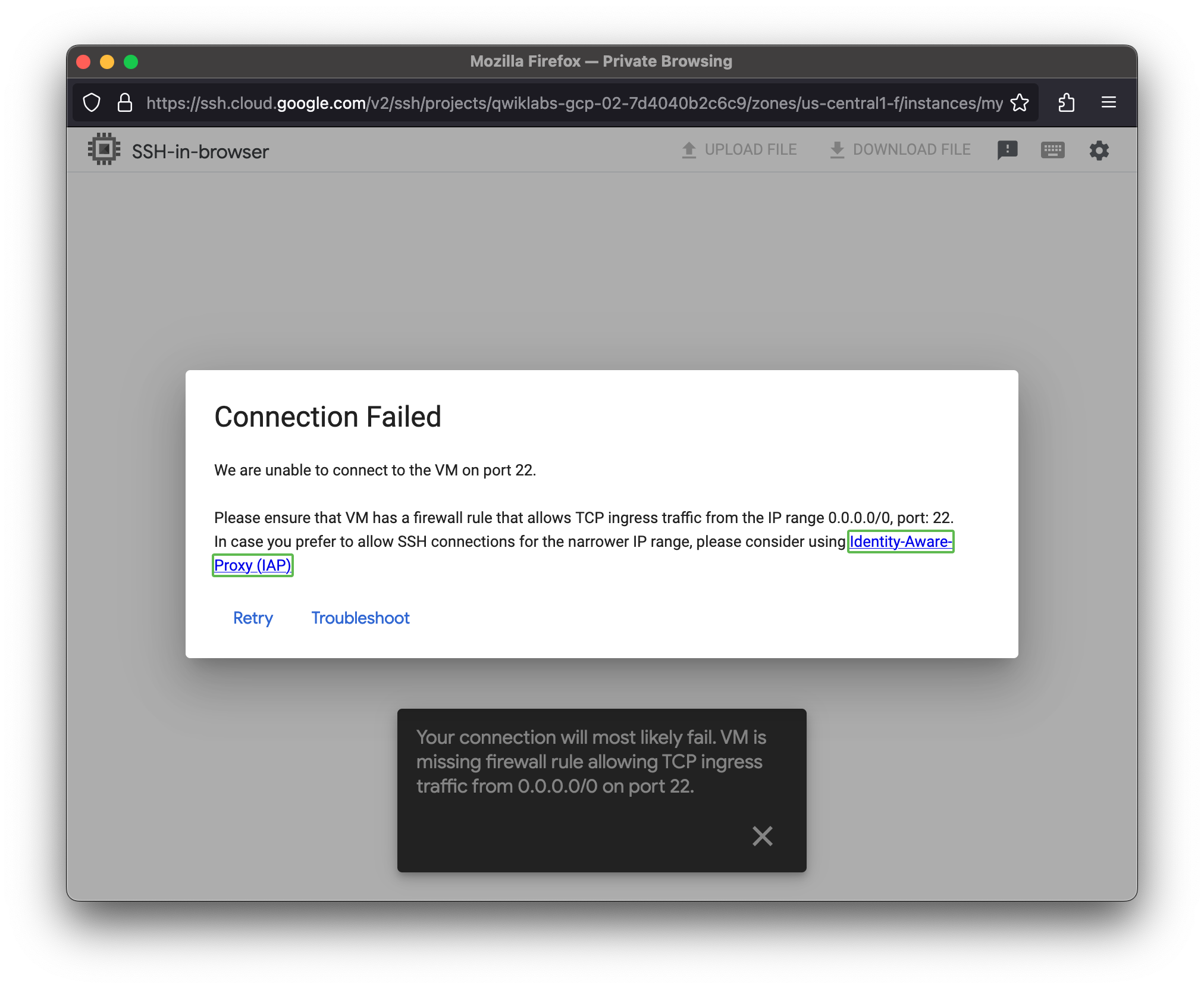
Remove the allow-ssh firewall rules
Remove the allow-ssh firewall rule and try to SSH to mynet-us-vm.
- On the Navigation menu (
), click VPC network > Firewall.
- Select the mynetwork-allow-ssh rule.
- Click Delete.
- Click Delete to confirm the deletion.
- Wait for the firewall rule to be deleted.
- On the Navigation menu, click Compute Engine > VM instances.
- For mynet-us-vm, click SSH to launch a terminal and connect.
In this lab, you explored the default network along with its subnets, routes, and firewall rules. You deleted the default network and determined that you cannot create any VM instances without a VPC network.
Thus, you created a new auto mode VPC network with subnets, routes, firewall rules, and two VM instances. Then you tested the connectivity for the VM instances and explored the effects of the firewall rules on connectivity.